| Structure Identification: |
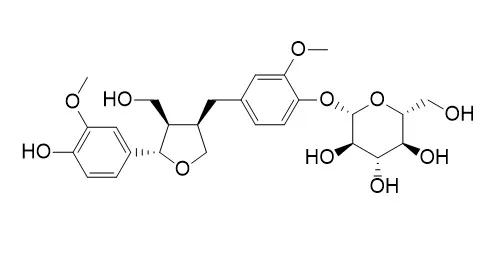
| J Agric Food Chem . 2001 Jun;49(6):2788-2798. | | Isolation and characterization of novel benzoates, cinnamates, flavonoids, and lignans from Riesling wine and screening for antioxidant activity[Pubmed: 11409967] | | A German Riesling wine has been fractionated with the aid of countercurrent chromatography. After purification by HPLC, the structures of 101 compounds were established by mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy. Seventy-three of the isolated compounds exhibited a phenolic or benzylic structure. Fifty-four compounds were reported for the first time as Riesling wine constituents. New compounds identified in this work included twelve benzoic and cinnamic acid derivatives. In addition to two isomeric (E)-caffeoyl ethyl tartrates, the glucose esters of (E)-cinnamic, (E)-p-coumaric, and (E)-ferulic acid, as well as the 4-O-glucosides of (E)- and (Z)-ferulic acid, have been identified for the first time in Riesling wine. The structures of two additional phenylpropanoids were elucidated as 3-hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-propan-1-one and 2,3-dihydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-propan-1-one. Moreover, two ethyl esters, i.e., ethyl protocatechuate and ethyl gallate, as well as the glucose ester of vanillic acid, were newly detected in Riesling wine. Novel representatives in the flavonoid group were dihydrokaempferol, dihydroquercetin, and four dihydroflavonol glycoconjugates, i.e., the 3-O-glucosides of dihydrokaempferol and dihydroquercetin, as well as the 3-O-xyloside and the 3'-O-glucoside of dihydroquercetin. Additionally, six novel lignans, i.e., Lariciresinol 4-O-glucoside, three isolariciresinol derivatives, and two secoisolariciresinols, as well as three neolignans were isolated. Structural elucidation of the newly isolated wine constituents is reported together with the determination of their antioxidant activity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)