| Kinase Assay: |
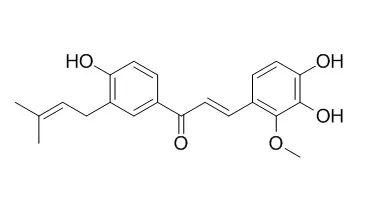
| Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Jul;10(7):769-76. | | Licochalcones suppress degranulation by decreasing the intracellular Ca2+ level and tyrosine phosphorylation of ERK in RBL-2H3 cells.[Pubmed: 20399908 ] | Mast cells play a key role in allergic inflammation by releasing various mediators, such as histamine, serotonin, leukotrienes and cytokines. A signaling cascade of events activated by stimulation with antigens contributes to the regulation of mast cell degranulation. While various anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic drugs have been developed that inhibit degranulation of mast cells, the inhibitory mechanism has been poorly understood. Licochalcone A (Lico A) is a retrochalcone isolated from the root of Xinjiang liquorice and has been reported to exhibit various biological activities such as anti-inflammatory activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We examined the effects of Lico A and related chalcones on degranulation in a rat basophilic leukemia cell line, RBL-2H3. Whereas Lico A and licochalcone C (Lico C) exhibited inhibitory activity with cytotoxicity, Licochalcone D (Lico D) significantly inhibited the degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells with low cytotoxicity. Moreover, Lico D significantly inhibited the Ca2+ influx and phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) and MEK.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Lico D inhibits mast cell degranulation via the inhibition of both extracellular Ca2+ influx and activation of the MEK-ERK pathway. | | Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 Apr;9(4):499-507. | | Glycyrrhiza inflata-derived chalcones, Licochalcone A, Licochalcone B and Licochalcone D, inhibit phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 in LPS signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 19291859] | Licorice root has been used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of gastric ulcer, bronchial asthma and inflammation. Licochalcone A is a major component of Xinjiang licorice, Glycyrrhiza inflata. Previously we showed that Licochalcone A significantly inhibited LPS-induced NF-kappaB transcriptional activation by abrogating the phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 at serine 276.
CONCLUSIONS:
Glycyrrhiza inflata contains not only Licochalcone A but also Licochalcone B, Licochalcone C, Licochalcone D, Echinatin and Isoliquiritigenin, harboring the common structure of chalcones. No chalcones had any effect on LPS-induced IkappaB degradation, nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity of NF-kappaB p65; however, we observed that Licochalcone B and Licochalcone D significantly inhibited LPS-induced phosphorylation at serine 276 and transcriptional activation of NF-kappaB, the same as Licochalcone A. Interestingly, we also found that Licochalcone A, Licochalcone B and Licochalcone D effectively inhibited LPS-induced activation of PKA, which is required for the phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 at serine 276. Consequently, Licochalcone B and Licochalcone D significantly reduced the LPS-induced production of NO, TNFalpha and MCP-1. On the other hand, Licochalcone C, Echinatin and Isoliquitigenin failed to inhibit LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that the anti-inflammatory effect of Glycyrrhiza inflata is ascribable to the potent inhibition of NF-kappaB by Licochalcone A, Licochalcone B and Licochalcone D. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)