| Biochemical Pharmacology, 2003, 66(10):1925-1933. |
| Suppression of RelA/p65 transactivation activity by a lignoid manassantin isolated from Saururus chinensis.[Reference: WebLink] |
In our search for NF-κB inhibitors from natural resources, we have previously identified two structurally related dilignans, Manassantin A and manassantin B as specific inhibitors of NF-κB activation from Saururus chinensis. However, their molecular mechanism of action remains unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We here demonstrate that Manassantin A and manassantin B are potent inhibitors of NF-κB activation by the suppression of transciptional activity of RelA/p65 subunit of NF-κB. These compounds significantly inhibited the induced expression of NF-κB reporter gene by LPS or TNF-α in a dose-dependent manner. However, these compounds did not prevent the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB assessed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay as well as the induced-degradation of IκB-α protein by LPS or TNF-α. Further analysis revealed that Manassantin A and manassantin B dose-dependently suppressed not only the induced NF-κB activation by overexpression of RelA/p65, but also transactivation activity of RelA/p65. Furthermore, treatment of cells with these compounds prevented the TNF-α-induced expression of anti-apoptotic NF-κB target genes Bfl-1/A1, a prosurvival Bcl-2 homologue, and resulted in sensitizing HT-1080 cells to TNF-α-induced cell death. Similarly, these compounds also suppressed the LPS-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and nitric oxide production.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, Manassantin A and manassantin B could be valuable candidate for the intervention of NF-κB-dependent pathological condition such as inflammation and cancer. |
| Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 2011, 115(1):84-88. |
| Manassantin A and B from Saururus chinensis inhibit interleukin-6-induced signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation in Hep3B cells.[Reference: WebLink] |
Inhibition of interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been postulated to be an effective therapy in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory diseases. The current study was performed to examine potential effects of Manassantin A and manassantin B isolated from Saururus chinensis on the IL-6-induced response to human hepatoma cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that Manassantin A and manassantin B inhibit signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) activity stimulated by IL-6. We also found that both compounds decreased IL-6-induced Stat3 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. Both compounds blocked suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS-3)-mRNA expression induced by IL-6. In addition, we found that Stat3 inhibitory effects of these compounds could be related to protein tyrosine phosphatase.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that Manassantin A and manassantin B could be useful remedies for treatment of inflammatory diseases by inhibiting IL-6 action. |
| Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2011, 34(11):1769-1772. |
| Manassantin A isolated from Saururus chinensis inhibits 5-lipoxygenase-dependent leukotriene C4 generation by blocking mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in mast cells.[Reference: WebLink] |
In this study, Manassantin A (Man A), an herbal medicine isolated from Saururus chinensis (S. chinensis), markedly inhibited 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO)-dependent leukotriene C(4) (LTC(4)) generation in bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) in a concentration-dependent manner.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the inhibition of LTC(4) generation by Man A, we assessed the effects of Man A on phosphorylation of cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Inhibition of LTC(4) generation by Man A was accompanied by a decrease in cPLA(2) phosphorylation, which occurred via the MAPKs including extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase-1/2 (ERK1/2) as well as p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the present study suggests the Man A represents a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of airway allergic-inflammatory diseases. |
| Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2014, 49(5):622-626. |
| A novel HIF-1 inhibitor--manassantin A derivative LXY6099 inhibits tumor growth.[Reference: WebLink] |
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is a key transcription factor on hypoxia responses in mammalian tissues. HIF-1 plays as a positive factor in solid tumor and leads to hypoxia-driven responses that enhance its downstream gene expression for tumor growth and survival. LXY6099 was obtained by the structural modification and optimization of Manassantin A (MA) as a high potent HIF-1 inhibitor.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antitumor activity of LXY6099 was observed in this study.
LXY6099 with an IC50 value of 2.46 x 10(-10) mol x L(-1) showed more sensitive inhibition activity to HIF-1 than that of MA detected by reporter gene assay (> 100 folds). It showed strong inhibition on the growth of human solid tumor cell lines. Furthermore, LXY6099 exhibited significant antitumor activity against established human tumor xenografts in nu/nu mice with treatment of MX-1 breast cancer.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, LXY6099 as a novel HIF-1 inhibitor could be further developed into anti-cancer agents. |


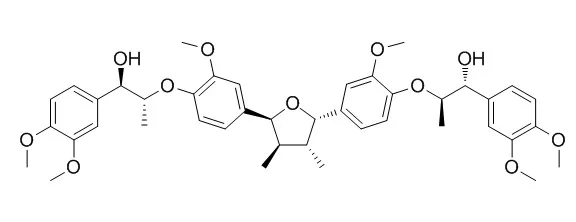



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)