| Description: |
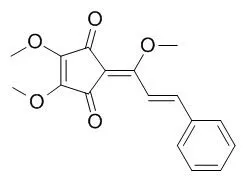
Methyllinderone is a human chymase inhibitor, it has antioxidant property, it also shows moderate to weak antifungal activities against various pathogenic fungi. Methyllinderone can inhibit farnesyl protein transferase with IC50 value of 55.3+/-4.1microM and selectively inhibit the growth of H-ras-transformed rat-2 cell lines with a GI50 value of 0.3 microM. Methyllinderone shows significant cytotoxicity against mouse melanoma (B16-F10), human acetabulum fibrosarcoma (HT1080), and choronic myelogenous leukemia (K562) cancer cell lines with ED(50) values of 2.2, 2.5, 8.3 mug/ml, respectively. |
| In vitro: |
| Nat. Prod. Sci., 2002, 8(3):100-2. | | Cytotoxicity of Lignans from Lindera erytheroca.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three lignans were isolated from a methanol extract of Lindera erytherocarpa Makino (Lauraceae) are evaluated in vitro cytotoxicity using three cancer cell line assay. The compounds were identified as Methyllinderone (1), linderone (2), and kanakugiol (3) by spectroscopic methods.
CONCLUSIONS:
Amongst the compounds, Methyllinderone (1) showed significant cytotoxicity against mouse melanoma (B16-FlO), human acetabulum fibrosarcoma (HT1080), and choronic myelogenous leukemia (K562) cancer cell lines with values of 2.2, 2.5, 8.3 , respectively. | | Planta Med. 2007 Jun;73(7):679-82. | | Inhibition of chitin synthase 2 and antifungal activity of lignans from the stem bark of Lindera erythrocarpa.[Pubmed: 17538872] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Potent chitin synthase 2 inhibitors, Methyllinderone (1), linderone (2) and kanakugiol (3) were isolated from the stem bark of L. erythrocarpa Makino (Lauraceae). These compounds inhibited chitin synthase 2 with IC(50) values of 23.3, 21.4 and 23.8 microg/mL, respectively. Methyllinderone (1) and linderone (2) exhibited no inhibitory activities for chitin synthases 1 and 3 from S. cerevisiae, and chitin synthase 1 from Candida albicans up to the concentration of 280 microg/mL, while kanakugiol (3) exhibited very weak activity against chitin synthase 1 of C. albicans with an IC(50) of 160 microg/mL. All of the compounds showed moderate to weak antifungal activities against various pathogenic fungi (MIC: 8 - >128 microg/mL) including Cryptococcus neoformans, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Colletotrichum lagenarium.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicate that these compounds are specific inhibitors of chitin synthase 2 and can potentially serve as antifungal agents. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)