| Description: |
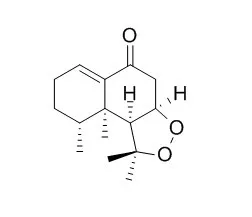
Nardosinone is an enhancer of nerve growth factor and possesses a wide range of pharmacological effects, including sedative, adaptogen-like, anti-depressive, anti-leukemic, anti-tumorous, and anti-trypanosomal activities. It has a wide spectrum of targets including PI3K,Akt,MEK,ERK, PKA, MAPK.
|
| In vitro: |
| J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013 Dec;33(6):822-6. | | Nardosinone protects H9c2 cardiac cells from angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy.[Pubmed: 24337842] | Pathological cardiac hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II (AngII) can subsequently give rise to heart failure, a leading cause of mortality. Nardosinone is a pharmacologically active compound extracted from the roots of Nardostachys chinensis, a well-known traditional Chinese medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to investigate the effects of Nardosinone on AngII-induced cardiac cell hypertrophy and the related mechanisms, the myoblast cell line H9c2, derived from embryonic rat heart, was treated with Nardosinone (25, 50, 100, and 200 μmol/L) or AngII (1 μmol/L). Then cell surface area and mRNA expression of classical markers of hypertrophy were detected. The related protein levels in PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MEK/ERK signaling pathways were examined by Western blotting. It was found that pretreatment with Nardosinone could significantly inhibit the enlargement of cell surface area induced by AngII. The mRNA expression of ANP, BNP and β-MHC was obviously elevated in AngII-treated H9c2 cells, which could be effectively blocked by Nardosinone at the concentration of 100 μmol/L. Further study revealed that the protective effects of Nardosinone might be mediated by repressing the phosphorylation of related proteins in PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signaling pathways.
CONCLUSIONS:
It was suggested that the inhibitory effect of Nardosinone on Ang II-induced hypertrophy in H9c2 cells might be mediated by targeting PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. | | PLoS One. 2014 Mar 10;9(3):e91260. | | Nardosinone improves the proliferation, migration and selective differentiation of mouse embryonic neural stem cells.[Pubmed: 24614893] | In this study, we investigated the impact of Nardosinone, a bioactive component in Nardostachys root, on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The neural stem cells were isolated from cerebrums of embryonic day 14 CD1 mice. The proliferation of cells was monitored using the cell counting kit-8 assay, bromodeoxyuridine incorporation and cell cycle analysis. Cell migration and differentiation were investigated with the neurosphere assay and cell specific markers, respectively. The results showed that Nardosinone promotes cells proliferation and increases cells migration distance in a dose-dependent manner. Nardosinone also induces the selective differentiation of neural stem cells to neurons and oligodendrocytes, as indicated by the expression of microtubule-associated protein-2 and myelin basic protein, respectively. Nardosinone also increases the expression of phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phospho-cAMP response element binding protein during proliferation and differentiation.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, this study reveals the regulatory effects of Nardosinone on neural stem cells, which may have significant implications for the treatment of brain injury and neurodegenerative diseases. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)