| Description: |
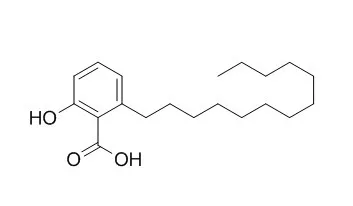
Ginkgolic acid C13:0 has a wide antimicrobial spectrum against E.coli and bacillus subtilis who are bacterias, and penicillium, penicillum purpurogenum, penicillium camemberti and aspergillus niger who are fungis, and the MIC of it against E.coli, bacillus subtilis and penicillium is 7.5, 15, 25 mg/mL seperately. It is a natural anticariogenic agent in that it exhibits antimicrobial activity against S. mutans and suppresses the specific virulence factors associated with its cariogenicity. Ginkgolic acid C13:0 exhibits the high α-glucosidase inhibitory activity; Ginkgolic acid C13:0 represents a new kind of molluscicide agent , it has a pronounced effect on snail mitochondria with gross ultrastructural changes. |
| Targets: |
Antifection | α-glucosidase |
| In vitro: |
| Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology. 2015, 15(3):207-15. | | Purification, identification and the antimicrobial activity of ginkgolic acids in ginkgo seeds.[Reference: WebLink] | Ginkgo seeds were used as materials in this experiment, Ginkgolic acids in ginkgo seeds were extracted by ethanol, and the ethanol extract were further extracted with petroleum ether.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The purification process of the ginkgolic acids were studied, and the compositions and contents were analyzed and detected by the methods of combination of HPLC and LC-MS. And two bacterias and four fungis were used for tested strains, the antimicrobial activity of ginkgolic acids were tested and the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) were determined separately. The results show that taking 89:1:11 system of petroleum ether, ethyl ether, and methanol as eluents, at 1.2 mL/min velocity, the effect of the silica gel column chromatography purification is the better. HPLC and LC -MS analysis showed that ginkgolic acids in ginkgo seeds consists chiefly of Ginkgolic acid C13:0, C15:1, C17:2, C15:0, C17:1. The content of ginkgolic acids in skimmed ginkgo powder is 0.11 g/kg by the C13:0, C15:1, C17:1 and the content of Ginkgolic acid C13:0, C15:1, C17:1 is 0.013, 0.042, 0.055 g/kg separately.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antimicrobial tests showed that ginkgolic acids had a wide antimicrobial spectrum against E.coli and bacillus subtilis who are bacterias, and penicillium, penicillum purpurogenum, penicillium camemberti and aspergillus niger who are fungis. And the MIC of the ginkgolic acids against E.coli, bacillus subtilis and penicillium is 7.5, 15, 25 mg/mL seperately. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Aquaculture, 2009, 297(1-4):38-43. | | In vivo assessment of anthelmintic efficacy of ginkgolic acids (C13:0, C15:1) on removal of Pseudodactylogyrus in European eel[Reference: WebLink] | Pseudodactylogyrus is a significant monogenean parasite of the gills of aquacultured European eels, and can cause severe gill pathology.
In this study, effects of the crude extracts, fractions and compounds of exopleura of Ginkgo biloba against Pseudodactylogyrus were investigated under in vivo conditions by bio-assay guided isolation method.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four solvents (petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water) were applied for the extraction of exopleura of G. biloba. Among them, only the petroleum ether extract showed strong activity and therefore, subjected to further separation and purification using various chromatographic techniques. Two compounds showing potent activity were identified by comparing spectral data (IR, NMR, and EI-MS) with literature values to be Ginkgolic acid C13:0 and C15:1. They were found to be 100% effective at the concentration of 2.5 mg l- 1 and 6.0 mg l- 1, with ED50 values of 0.72 mg l- 1 and 2.88 mg l- 1, respectively. In the 5-days safety test, Ginkgolic acid C13:0 and C15:1 were shown to be safe for healthy juvenile eels when the concentration were up to 10.0 and 18.0 mg l- 1, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The two compounds exhibited potential results and can be explored as plant-derived antiparasitic for the control of Pseudodactylogyrus. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)