| Description: |
Procyanidin C1 has anti-inflammatory effects, can inhibit IKKb activity in vitro and reduce the LPS-induced production of ROS, thus, it exerts the anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting ERK1/2 and IKKb activity. Procyanidin C1 could be useful as a lead compound to develop inhibitors of cancer metastasis and other diseases related to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Procyanidin C1 may represent a novel and potentially therapeutically relevant compound for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, it -induced vasorelaxation is associated with the activation of the calcium-dependent NO/cGMP pathway, involving potassium channel activation. |
| In vitro: |
| Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2008;147(3):213-21. | | Procyanidin C1 from apple extracts inhibits Fc epsilon RI-mediated mast cell activation.[Pubmed: 18594151] | Polyphenol-enriched fractions, which are extracted from unripe apples (Rosaceae, Malus spp.), consisting of procyanidins (polymers of catechins) are known to have an anti-allergenic effect on patients with various allergic diseases. Although it has been reported that apple extracts inhibit histamine release from mast cells, the molecular mechanisms for this anti-allergenic effect are not well understood. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which apple extracts induce their anti-allergenic effects, the effects of purified apple extract components on high-affinity receptors for IgE (Fc epsilon RI)-mediated mast cell activation were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The anti-allergic effect of oral administration of apple procyanidin extracts on passive cutaneous anaphylactic responses of BALB/c mice was assessed. We evaluated the effects of Procyanidin C1 (PC1) [epicatechin-(4beta-->8)-epicatechin-(4beta-->8)-epicatechin], a component of the procyanidin fraction, on mouse bone-marrow-derived mast cell degranulation, cytokine production, protein tyrosine phosphorylation and on the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) of cells stimulated by Fc epsilon RI cross-linking in vitro. In an in vivo study, oral administration of the procyanidin fraction suppressed the mast-cell-dependent allergic reaction. In in vitro studies, Procyanidin C1 dose-dependently decreased Fc epsilon RI-mediated degranulation and cytokine production of mast cells. Furthermore, Procyanidin C1 inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk and linker for activation of T cells, and the ROS generation in stimulated mast cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Procyanidin C1 suppresses Fc epsilon RI-mediated mast cell activation by inhibiting intracellular signaling pathways. These observations provide evidence for the anti-allergenic effects of the procyanidin-enriched apple extract. | | Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:365258. | | Immunosuppressive Effects of A-Type Procyanidin Oligomers from Cinnamomum tamala.[Pubmed: 25530780] | Cinnamon barks extracts have been reported to regulate immune function; however, the component(s) in cinnamon barks responsible for this effect is/are not yet clear. The aim of this study is to find out the possible component(s) that can be used as therapeutic agents for immune-related diseases from cinnamon bark.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the immunosuppressive effects of fraction (named CT-F) and five procyanidin oligomers compounds, cinnamtannin B1, cinnamtannin D1 (CTD-1), parameritannin A1, procyanidin B2, and Procyanidin C1, from Cinnamomum tamala or Cinnamomum cassia bark were examined on splenocytes proliferation model induced by ConA or LPS. Then, the effects of activated compound CTD-1 on cytokine production and 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) induced delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) response were detected to evaluate the immunosuppressive activity of CTD-1. It was found that CT-F and CTD-1 significantly inhibited the splenocyte proliferation induced by ConA or LPS. CTD-1 dose-dependently reduced the level of IFN-γ and IL-2 and intensively suppressed DNFB-induced DTH responses.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that the immunosuppressive activities of cinnamon bark are in part due to procyanidin oligomers. CTD-1 may be a potential therapeutic agent for immune-related diseases. | | Nat Prod Res . 2020 Nov;34(22):3267-3274. | | A comparative anticancer study on procyanidin C1 against receptor positive and receptor negative breast cancer[Pubmed: 30618284] | | Abstract
Albezia odoratissima has many health benefits. The present study investigated the isolation, characterization and anticancer activity of Procyanidin C1 from A. odoratissima bark. Procyanidin C1 was isolated and characterized by IR, 13C NMR, 1H NMR and LC-MS spectroscopic studies. Anticancer property of Procyanidin C1 was explored by studying the expression of checkpoint kinases, Bcl-2 and BAX, cell cycle, DNA damage and caspase 3 and 9 levels. Procyanidin C1 exhibited significant cytotoxicity against TNBC (MDA-MB- 231), hormone positive (MCF-7) cell lines. Its IC50 value is comparable to tamoxifen towards MDA-MB- 231 cell line, but considerably higher towards MCF-7 cell line. Procyanidin C1 induced DNA damage, cell cycle arrest and enhanced the expression of checkpoint kinases. Procyanidin C1 decreased the level of Bcl-2 but increased the BAX, caspase 3 and 9 expression in cancer cells. This study indicates the antiproliferative property of Procyanidin C1 against breast cancer cells by inducing apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; NMR; breast cancer; cell cycle arrest; Procyanidin C1. |
|


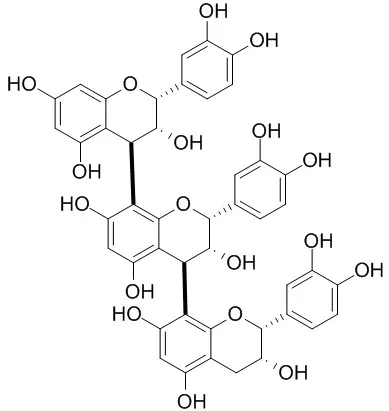



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)