| Structure Identification: |
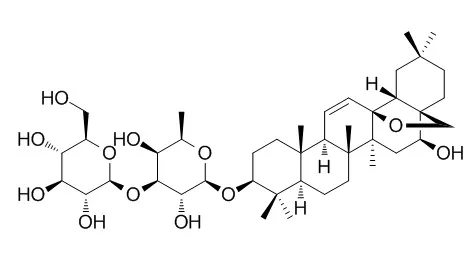
| Biomedical Chromatography, 2018, 32(2):e4044. | | Characterization and discrimination of raw and vinegar-baked Bupleuri Radix based on UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS coupled with multivariate statistical analysis.[Reference: WebLink] | Bupleuri Radix is a commonly used herb in clinic, and raw and vinegar-baked Bupleuri Radix are both documented in the Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China. According to the theories of traditional Chinese medicine, Bupleuri Radix possesses different therapeutic effects before and after processing. However, the chemical mechanism of this processing is still unknown.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry coupled with multivariate statistical analysis including principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least square-discriminant analysis was developed to holistically compare the difference between raw and vinegar-baked Bupleuri Radix for the first time. As a result, 50 peaks in raw and processed Bupleuri Radix were detected, respectively, and a total of 49 peaks chemical compounds were identified. Saikosaponin a, saikosaponin d, saikosaponin b3 , Saikosaponin E, saikosaponin c, saikosaponin b2 , saikosaponin b1 , 4"-O-acetyl-saikosaponin d, hyperoside and 3', 4'-dimethoxy quercetin were explored as the potential markers of raw and vinegar-baked Bupleuri Radix.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study has been successfully applied for global analysis of raw and vinegar processed samples. Furthermore, the underlying hepatoprotective mechanism of Bupleuri Radix was predicted, which was related to the changes of chemical profiling. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)