| Description: |
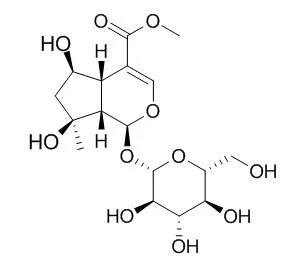
Shanzhiside methylester reduces neuropathic pain by activating spinal GLP-1 receptors and subsequently stimulating microglial β-endorphin expression via the p38 MAPK signaling. |
| Targets: |
p38MAPK | GLP-1 receptor |
| In vitro: |
| Neuropharmacology . 2016 Feb;101:98-109. | | Shanzhiside methylester, the principle effective iridoid glycoside from the analgesic herb Lamiophlomis rotata, reduces neuropathic pain by stimulating spinal microglial β-endorphin expression[Pubmed: 26363192] | | Abstract
Lamiophlomis rotata (L. rotata, Duyiwei) is an orally available Tibetan analgesic herb widely prescribed in China. Shanzhiside methylester (SM) is a principle effective iridoid glycoside of L. rotata and serves as a small molecule glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. This study aims to evaluate the signal mechanisms underlying SM anti-allodynia, determine the ability of SM to induce anti-allodynic tolerance, and illustrate the interactions between SM and morphine, or SM and β-endorphin, in anti-allodynia and anti-allodynic tolerance. Intrathecal SM exerted dose-dependent and long-lasting (>4 h) anti-allodynic effects in spinal nerve injury-induced neuropathic rats, with a maximal inhibition of 49% and a projected ED50 of 40.4 μg. SM and the peptidic GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide treatments over 7 days did not induce self-tolerance to anti-allodynia or cross-tolerance to morphine or β-endorphin. In contrast, morphine and β-endorphin induced self-tolerance and cross-tolerance to SM and exenatide. In the spinal dorsal horn and primary microglia, SM significantly evoked β-endorphin expression, which was completely prevented by the microglial inhibitor minocycline and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor SB203580. SM anti-allodynia was totally inhibited by the GLP-1 receptor antagonist exendin(9-39), minocycline, β-endorphin antiserum, μ-opioid receptor antagonist CTAP, and SB203580. SM and exenatide specifically activated spinal p38 MAPK phosphorylation. These results indicate that SM reduces neuropathic pain by activating spinal GLP-1 receptors and subsequently stimulating microglial β-endorphin expression via the p38 MAPK signaling. Stimulation of the endogenous β-endorphin expression may be a novel and effective strategy for the discovery and development of analgesics for the long-term treatment of chronic pain.
Keywords: Anti-allodynia; Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor; Microglia; Shanzhiside methylester (SM); p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); β-endorphin. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Neuropharmacology. 2016 Feb;101:98-109 | | Shanzhiside methylester, the principle effective iridoid glycoside from the analgesic herb Lamiophlomis rotata, reduces neuropathic pain by stimulating spinal microglial β-endorphin expression.[Pubmed: 26363192 ] | Lamiophlomis rotata (L. rotata, Duyiwei) is an orally available Tibetan analgesic herb widely prescribed in China. Shanzhiside methylester (SM) is a principle effective iridoid glycoside of L. rotata and serves as a small molecule glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. This study aims to evaluate the signal mechanisms underlying SM anti-allodynia, determine the ability of SM to induce anti-allodynic tolerance, and illustrate the interactions between SM and morphine, or SM and β-endorphin, in anti-allodynia and anti-allodynic tolerance.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Intrathecal SM exerted dose-dependent and long-lasting (>4 h) anti-allodynic effects in spinal nerve injury-induced neuropathic rats, with a maximal inhibition of 49% and a projected ED50 of 40.4 μg. SM and the peptidic GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide treatments over 7 days did not induce self-tolerance to anti-allodynia or cross-tolerance to morphine or β-endorphin. In contrast, morphine and β-endorphin induced self-tolerance and cross-tolerance to SM and exenatide. In the spinal dorsal horn and primary microglia, SM significantly evoked β-endorphin expression, which was completely prevented by the microglial inhibitor minocycline and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor SB203580. SM anti-allodynia was totally inhibited by the GLP-1 receptor antagonist exendin(9-39), minocycline, β-endorphin antiserum, μ-opioid receptor antagonist CTAP, and SB203580. SM and exenatide specifically activated spinal p38 MAPK phosphorylation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that SM reduces neuropathic pain by activating spinal GLP-1 receptors and subsequently stimulating microglial β-endorphin expression via the p38 MAPK signaling. Stimulation of the endogenous β-endorphin expression may be a novel and effective strategy for the discovery and development of analgesics for the long-term treatment of chronic pain. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)