| In vitro: |
| J Comp Pathol. 1990 Aug;103(2):169-82. | | Myopathy in cattle induced by alkaloid extracts from Thermopsis montanta, Laburnum anagyroides and a Lupinus sp.[Pubmed: 2246392] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A purified alkaloid preparation containing N-methylcytisine, cytisine, 5,6-dehydrolupanine, Thermopsine and anagyrine from Thermopsis montana induced prolonged recumbency and microscopic acute hyaline skeletal myodegeneration with myofibre regeneration in cattle similar in type and severity to that induced by Thermopsis montanta plant material. This indicates that the alkaloid(s) of Thermopsis montana are responsible for the myopathy caused by the plant. An alkaloid preparation containing mostly anagyrine from a Lupinus sp. and an alkaloid preparation containing only cytisine from Laburnum anagyroides each caused microscopic skeletal muscle degeneration and necrosis similar to, but less severe than, the alkaloid extract from T. montana, but without clinical recumbency. Dosage and severity of response suggest that neither of those two alkaloids alone can account for the effects induced by Thermopsis.
CONCLUSIONS:
The data suggest that quinolizidine alkaloids with a alpha-pyridone A-ring may be responsible for the lesions and that individual alpha-pyridones may have additive effects. | | Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Aug;7(8):999-1003. | | Quinolizidine alkaloids from Sophora velutina subsp. zimbabweensis (Fabaceae: Sophoreae).[Pubmed: 22978215] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
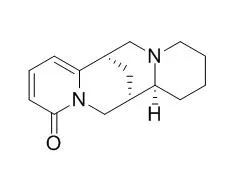
Three novel quinolizidine alkaloids, N-methylenehydroxycytisine (1), 6,7-dihydroxylupanine (2), and velutinine (3) have been isolated from the fruits and pods (1 and 2) and stem bark (3) of Sophora velutina subsp. zimbabweensis along with the known quinolizidine alkaloids, 7-hydroxylupanine (4), Thermopsine (5), N-methylcytisine (6), cytisine (7), an aromatic ester, methyl-3-(3',4'-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-propenoate (8) and the triterpenoids, lup-20(29)-ene-3beta-ol (9) and 12-oleanen-3-one (10).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 6 and 10 showed good antibacterial activity against E. faecalis, with MIC values of 20.8 and 10.9 microg mL(-1), respectively. The other compounds tested exhibited low to moderate antibacterial activity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)