| Kinase Assay: |
| South African Journal of Botany Volume 146, May 2022, Pages 254-261 | | Simultaneous characterization of nine isolated flavonoids in Iranian Dracocephalum species and in silico study of their inhibitory properties against MTH1 enzyme[Reference: WebLink] | | Dracocephalum L. is a well-known aromatic and medicinal plant genus in the Mint family. Some species of the genus such as D. kotschyi (DK) are widely used in Iranian folk medicine as tonic and carminative, as well as for relieves of headache, stomachache, and liver ailments. The present study was aimed to: isolate and determine some bioactive flavonoids from DK, evaluate their content in some Iranian Dracocephalum species, and assess their inhibitory activity and molecular dynamics against Human mutT homolog 1 (MTH1) enzyme. Aerial flowering parts of eight Iranian native Dracocephalum species were collected from different regions of Iran. The flavonoids of DK were comprehensively isolated by column chromatography, and then characterized by NMR and MS techniques. For simultaneous determination of flavonoids in methanol extract of the Dracocephalum studied species, a reversed-phase HPLC-DAD method was developed. Luteolin, apigenin, xanthomicrol, calycopterin, ermanin and three newly isolated flavonoids including circilineol, 5-demethylsinenstin, cirsimaritin and 5,7,4′-trihydroxy 3,3′-dimethoxyflavone were characterized in DK. Simultaneous determination of nine flavonoids in eight Iranian Dracocephalum species exerted the highest amount of xanthomicrol (4430±1.8 μg/g DW) and 5-Demethylsinensetin (766.2±0.4 μg/g DW) in D. polychaetum and D. aucheri, respectively. Our study showed, different species with similar morphology have different flavonoid profile. To have a molecular insight into their effectiveness in cancer inhibition, Gaussian 03, GROMACS 5.2, and Pymol software were exploited to optimize, simulate, and dock them against MTH1 enzyme, respectively. Molecular docking study revealed that xanthomicrol and 5-demethylsinenstin could tightly bind to MTH1 enzyme via different hydrogen bonds in the active site of the protein. Xanthomicrol and 5-demethylsinenstin, the two flavonoids with stronger bonds with MTH1 enzyme, could be considered as reliable pharmacologically active ingredients against the cancers involving MTH1 activity. |
|
| Cell Research: |
| Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry May15 (2007) 3381–3389 | | Isolation and syntheses of polymethoxyflavones and hydroxylated polymethoxyflavones as inhibitors of HL-60 cell lines[Pubmed: 17391969] | | Fifteen polymethoxyflavones (PMFs) and hydroxylated PMFs were isolated from sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) peel extract and synthesized to investigate their biological activity. All obtained compounds were tested in HL-60 cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis induction assays. While some PMFs and hydroxylated PMFs had moderate anti-carcinogenic activities, 5-hydroxy-6,7,8,3',4'-pentamethoxyflavone and 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone showed strong inhibitory activities against the proliferation and induced apoptosis of HL-60 cell lines. | | Pharm Biol . 2016 Oct;54(10):2188-2195. | | Trypanocidal and leishmanicidal activities of flavonoids isolated from Stevia satureiifolia var. satureiifolia[Pubmed: 26983579] | | Context: Chagas’ disease and leishmaniasis produce significant disability and mortality with great social and economic impact. The genus Stevia (Asteraceae) is a potential source of antiprotozoal compounds.
Objective: Aerial parts of four Stevia species were screened on Trypanosoma cruzi. Stevia satureiifolia (Lam.) Sch. Bip. var. satureiifolia (Asteraceae) dichloromethane extract was selected for a bioassay-guided fractionation in order to isolate its active compounds. Additionally, the antileishmanial activity and the cytotoxicity of these compounds on mammalian cells were assessed.
Materials and methods: The dichloromethane extract was fractionated by column chromatography. The isolated compounds were evaluated using concentrations of 0–100 μg/mL on T. cruzi epimastigotes and on Leishmania braziliensis promastigotes for 72 h, on trypomastigotes and amastigotes of T. cruzi for 24 h and 120 h, respectively. The compounds’ cytotoxicity (12.5–500 μg/mL) was assessed on Vero cells by the MTT assay. The structure elucidation of each compound was performed by spectroscopic methods and HPLC analysis.
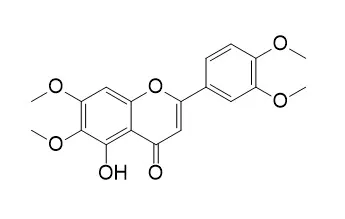
Results: The dichloromethane extracts of Stevia species showed significant activity on T. cruzi epimastigotes. The flavonoids eupatorin (1.3%), cirsimaritin (1.9%) and 5-desmethylsinensetin (1.5%) were isolated from S. satureiifolia var. satureiifolia extract. Eupatorin and 5-desmethylsinensetin showed IC50 values of 0.2 and 0.4 μg/mL on T. cruzi epimastigotes and 61.8 and 75.1 μg/mL on trypomastigotes, respectively. The flavonoid 5-desmethylsinensetin showed moderate activity against T. cruzi amastigotes (IC50 value = 78.7 μg/mL) and was the most active compound on L. braziliensis promastigotes (IC50 value = 37.0 μg/mL). Neither of the flavonoids showed cytotoxicity on Vero cells, up to a concentration of 500 μg/mL. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)