| Animal Research: |
| Archives for Dermatological Research, 1986, 278(5):347-351. | | The carcinogenic properties of topical PUVA. A lifelong study in mice.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The tumorigenic properties of topical methoxsalen (8-MOP) and Trioxsalen (TMP) plus ultraviolet light A (UVA) were studied in NMRI female mice. The animals were treated three times weekly for 9 months, and followed up for 18 months. Acetonic solutions of TMP (0.1 mg in 0.2 ml) and 8-MOP (0.6 mg in 0.2 ml) were applied to the shaved back skin of the mice and irradiated with UVA. The doses needed to elicit equivalent phototoxic effects were 0.29 J/cm 2 in the TMP group and 1.09 J/cm 2 in the 8-MOP group. Papillomas, keratoacanthomas, and squamous cell carcinomas developed in the 8-MOP group only, and the first tumor was seen at 10 months after the beginning of the study.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that the carcinogenicity of these two modes of photochemotherapy may differ. |
|
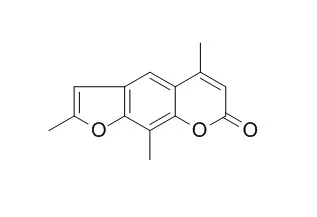
| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture, 2007, 87(11):2152-2163. | | Analysis of furanocoumarins in vegetables (Apiaceae) and citrus fruits (Rutaceae).[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Several alternative approaches applicable for the analysis of furanocoumarins, toxic components occurring in some fruits and vegetables representing both Apiaceae and Rutaceae families, were tested in our study. Limits of detection (LODs) for angelicin, psoralen, bergapten, xanthotoxin, Trioxsalen, isopimpinellin, sphondin, pimpinellin and isobergapten obtained by GC/MS (SIM) were in the range 0.01-0.08 µg g-1. Slightly higher LODs (0.02-0.20 µg g-1) were achieved by LC/MS-MS. The latter is the only alternative for analysis of bergamottin (LOD = 0.01 µg g-1) in citrus fruits because this furanocoumarin is unstable under GC conditions. Regardless of the determination step used, the repeatability of the measurements (expressed as RSD) did not exceed 10%.
CONCLUSIONS:
As shown in our study the levels of furanocoumarins in celery, celeriac, parsnip, carrot, lemon and other foods obtained at a retail market varied over a wide range; the highest contents were determined in parsnip, while the levels of these toxins in carrots and citrus pulps were relatively low. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)