| In vitro: |
| Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2002,50(6):760-765. | | Withanolide Derivatives from the Roots of Withania somnifera and Their Neurite Outgrowth Activities.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Five new withanolide derivatives (1, 9—12) were isolated from the roots of Withania somnifera together with fourteen known compounds (2—8, 13—19). On the basis of spectroscopic and physiochemical evidence, compounds 1 and 9—12 were determined to be (20S,22R)-3α,6α-epoxy-4β,5β,27-trihydroxy-1-oxowitha-24-enolide (1), 27-O-β-D-glucopyranosylpubesenolide 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside (withanoside VIII, 9), 27-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosylpubesenolide 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside (withanoside IX, 10), 27-O-β-D-glucopyranosylpubesenolide 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (withanoside X, 11), and (20R,22R)-1α,3β,20,27-tetrahydroxywitha-5,24-dienolide 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (withanoside XI, 12).
CONCLUSIONS:
Of the isolated compounds, 1, withanolide A (2), (20S,22R)-4β,5β,6α,27-tetrahydroxy-1-oxowitha-2,24-dienolide (6), Withanoside IV (14), withanoside VI (15) and coagulin Q (16) showed significant neurite outgrowth activity at a concentration of 1 μM on a human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. | | Life Sciences, 2003, 74(1):125-132. | | Growth inhibition of human tumor cell lines by withanolides from Withania somnifera leaves.[Reference: WebLink] | Ayurvedic medicines prepared in India consist of Withania somnifera roots as one of the main ingredients. It is consumed as a dietary supplement around the world. The leaves of W. somnifera were used in the treatment of tumors and inflammation in several Asian countries.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We have isolated twelve withanolides such as withaferin A (1), sitoindoside IX (2), 4-(1-hydroxy-2, 2-dimethylcyclpropanone)-2, 3-dihydrowithaferin A (3), 2, 3-dihydrowithaferin A (4), 24, 25-dihydro-27-desoxywithaferin A (5), physagulin D (1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl- (1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (6), 27-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylphysagulin D (7), physagulin D (8), Withanoside IV (9), and 27-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylviscosalactone B (10), 4, 16-dihydroxy-5beta, 6beta-epoxyphysagulin D (11), viscosalactone B (12) from the leaves of this species. Compounds 1-12 and diacetylwithaferin A (13) were tested for their antiproliferative activity on NCI-H460 (Lung), HCT-116 (Colon), SF-268 (Central Nervous System; CNS and MCF-7 (Breast) human tumor cell lines. The inhibitory concentration to afford 50% cell viability (IC50) for these compounds was determined by MTT (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay.
CONCLUSIONS:
Withaferin A and its derivatives exhibited inhibitory concentrations (50%) ranging from 0.24 +/- 0.01 to 11.6 +/- 1.9 microg/mL. Viscosalactone B (12) showed the 50% inhibition at concentrations ranging from 0.32 +/- 0.05 to 0.47 +/- 0.15 microg/mL whereas its 27-O-glucoside derivative (10) exhibited IC50 between 7.9 +/- 2.9 and 17.3 +/- 3.9 microg/ml. However, Physagulin D type withanolides showed either weak or no activity at 30 microg/mL. Therefore, incorporation of withanolides in the diet may prevent or decrease the growth of tumors in human. |
|
| In vivo: |
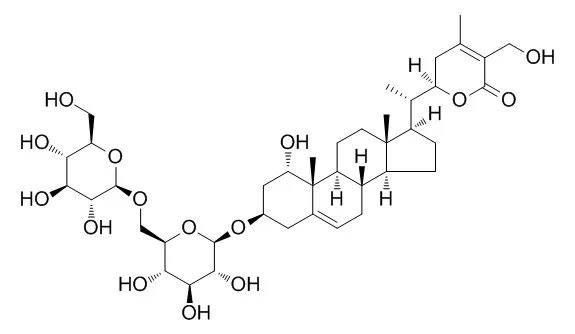
| European Journal of Neuroscience, 2006, 23(6):1417-1426. | | Withanoside IV and its active metabolite, sominone, attenuate Abeta(25-35)-induced neurodegeneration.[Reference: WebLink] | At the present, medication of dementia is limited to symptomatic treatments such as the use of cholinesterase inhibitors. To cure dementia completely, that is regaining neuronal function, reconstruction of neuronal networks is necessary.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Therefore, we have been exploring antidementia drugs based on reconstructing neuronal networks in the damaged brain and found that Withanoside IV (a constituent of Ashwagandha; the root of Withania somnifera) induced neurite outgrowth in cultured rat cortical neurons. Oral administration of Withanoside IV (10 micromol/kg/day) significantly improved memory deficits in Abeta(25-35)-injected (25 nmol, i.c.v.) mice and prevented loss of axons, dendrites, and synapses. Sominone, an aglycone of Withanoside IV, was identified as the main metabolite after oral administration of Withanoside IV. Sominone (1 microM) induced axonal and dendritic regeneration and synaptic reconstruction significantly in cultured rat cortical neurons damaged by 10 microM Abeta(25-35).
CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggest that orally administrated Withanoside IV may ameliorate neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease and that the active principle after metabolism is sominone. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)