| Structure Identification: |
| Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan (1998) 71(4) 781-787. | | Studies on Polyketide Metabolites of a Symbiotic Dinoflagellate, Symbiodinium sp.: A New C30 Marine Alkaloid, Zooxanthellamine, a Plausible Precursor for Zoanthid Alkaloids.[Reference: WebLink] | In studies on the biogenesis of vasocontrictive macrolides, zooxanthellatoxins isolated from a symbiotic dinoflagellate Symbiodinium sp., we have investigated metabolites of the dinoflagellate cultured under different conditions.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
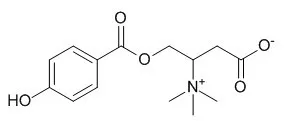
Four new compounds were isolated from 70% EtOH extract of the cells cultured in f/2 medium. Two betaines (Zooxanthellabetaine A and zooxanthellabetaine B) were obtained from a neutral fraction of n-BuOH soluble portion and the structure of zooxanthellabetaine-A was determined as 4-(4-hydroxybenzoyloxy)-3-(trimethylammonio)butyrate. The EtOAc soluble portion afforded a new C-30 alkaloid, zooxanthellamine, and a new ceramide, symbioramide-C16.
CONCLUSIONS:
The structural similarity of zooxanthellamine to zoanthid alkaloids, zoanthamines, suggested an algal origin of these zoanthamines, Zooxanthellamine might be derived biogenetically from a polyketide chain presumably started from a glycine unit, like other marine toxins such as zooxanthellatoxin and palytoxin. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)