The aerial parts of several Angelica species of the Apiaceae as natural medicine, are rich sources of various coumarins with biological, to a lesser extent, toxicological activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
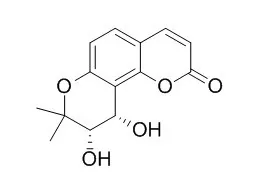
From the chloroform extract of the aerial parts of Angelica urumiensis MOZAFF. two new coumarins (1, 2), together with six known coumarins and two known flavonoids were isolated. On the basis of comprehensive spectroscopic analyses, including electron ionization-mass spectra (EI-MS), (1)H-NMR, (13)C-NMR, 1D nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE), distortionless enchancement by polarization transfer (DEPT), H, H correlation spectroscopy (COSY), heteronuclear multiple quantum coherence (HMQC), heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC), rotating frame Overhauser enhancement spectroscopy (ROESY) spectra and comparison with spectral data of known compounds, the structure of new compounds were established as pyranocoumarin dimmer (1) and (+)-8,9-dihydro-8-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-oxo-2H-furo[2,3-h]chromen-9-yl-3-methylbut-2-enoate (2). The eight known compounds (3-10) were isosamidin, laserpitin, pteryxin, isolaserpitin, cis-Khellactone, angelicin, genkwanin and salvigenin, respectively. These known structures are isolated from the aerial parts of A. urumiensis for the first time.
CONCLUSIONS:
Antioxidant activities of the two new coumarins were evaluated by using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay and exhibited a moderate antioxidant activity. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)