| In vitro: |
| Rec. Nat. Prod. 2019,13(1): 71-80. | | Chemical Constituents and Anti-influenza Viral Activity of the Leaves of Vietnamese Plant Elaeocarpus tonkinensis.[Reference: WebLink] | Various Elaeocarpus species including Elaeocarpus tonkinensis have been important medicinal plants
that used in traditional medication system and mainly used to cure nervous system-related disorders. However,
their antiviral potential has not been reported yet.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
During the screening of medicinal plant extracts with the
antiviral activity against influenza viruses, we found that E. tonkinensis extract has strong antiviral activity.
Through organic solvent partition and repeated column chromatography using SiO2, C-18 and Sephadex LH-20,
a total of nine compounds were purified from the methanol extract of E. tonkinensis. Their chemical structures
were determined by NMR and MS spectral data to be trolliamide (1), gallic acid (2), urolithin M-5 (3),
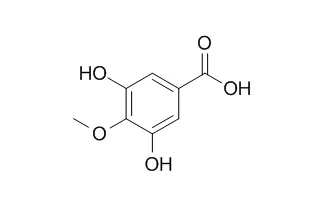
hydroquinone (4), 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (5), 3,5-Dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid (6), corilagin (7),
chebulagic acid (8), and shikimic acid (9). Their antiviral activity against influenza virus strains A/Puerto
Rico/8/34 (H1N1; PR8), A/Hong Kong/8/68 (H3N2; HK) and B/Lee/40 (Lee) was examined on the basis of
cytopathic effect (CPE) assay. Among them, compounds 2, 3, 4, 7, and 8 significantly inhibited viral replication
in a dose-dependent manner with EC50 values ranging from 7.8 to 59.6 μg/mL against influenza A and/or B
viruses with selectivity indices above 5.0.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study suggests that the botanical materials of E. tonkinensis could be promising inhibitors of influenza A and B viruses and applied to the development of a novel herbal medicine. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)