| In vitro: |
| Phytother Res. 2010 Mar;24(3):463-5. | | Protective effects of 3'-deoxy-4-O-methylepisappanol from Caesalpinia sappan against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat cortical cells.[Pubmed: 19777498] | To examine the neuroprotective effects of Caesalpinia sappan L., we tested its protection against the glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultured neurons.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
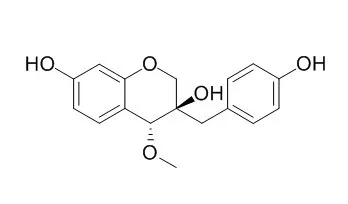
We found that an aqueous extract of this medicinal plant exhibited significant protection against glutamate-induced toxicity in primary cultured rat cortical cells. In order to clarify the neuroprotective mechanism(s) of this observed effect, isolation was performed to seek and identify active fractions and components. By such fractionation, two known compounds - sappanchalcone and 3'-Deoxy-4-O-methylepisappanol - were isolated from the methanol extracts from the air-dried and chipped C. sappan. Among these two compounds, 3'-Deoxy-4-O-methylepisappanol exhibited significant neuroprotective activities against glutamate-induced toxicity, exhibiting cell viability of about 50%, at concentrations ranging from 0.1 microM to 10 microM.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, the neuroprotective effect of C. sappan might be due to the inhibition of glutamate-induced toxicity by the protosappanin derivative it contains. | | J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2010 Oct;25(5):608-14. | | Antioxidant properties of benzylchroman derivatives from Caesalpinia sappan L. against oxidative stress evaluated in vitro.[Pubmed: 20105050] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antioxidant activity of extracts from Caesalpinia sappan L. (CSL) was studied in vitro by evaluating the total phenolics, measuring the antioxidant activity by TEAC, measuring the scavenging effects on reactive oxygen species (ROS) and on reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and measuring the inhibitory effect on Cu(2+)-induced human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation. The CSL extracts were found to have a potent scavenging activity against all of the reactive species tested, as well as an inhibitory effect on LDL oxidation, especially in the ethyl acetate (EA) fraction. Therefore, we isolated and identified benzylchroman derivatives sappanchalcone (1) and 3'-Deoxy-4-O-methylepisappanol (2) from the EA fraction of CSL and their antioxidant activities were evaluated.
CONCLUSIONS:
The studied CSL extracts and the compounds 1 and 2 were revealed to be very effective against the evaluated pro-oxidant species, including ROS and RNS. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)