| In vitro: |
| J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem.,2009, 52(6):663-7. | | Cytotoxic alkaloids from the wood of Picrasma quassioides.[Reference: WebLink] | Six alkaloid compounds were isolated from the chloroform soluble fraction of the methanolic extract of the wood of Picrasma quassioides Benn (Simarobaceae) as the cytotoxic components against the tumor cell lines, U937 and HepG2.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
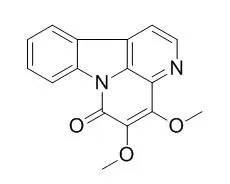
The compounds were identified as 4,9-dimethoxy-1-vinyl-γ-carboline (1), 1-carbomethoxy-β-carboline (2), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (3), 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one (4), 3-methoxycanthin-5,6-dione (5) and 4,8-dimethoxy-1-vinyl-β-carboline (6) by spectroscopic analysis. Among them, compound 5 showed the most potent cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner against the two tumor cell lines.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report of the cytotoxic effect of those isolated compounds 1-5 on U937 and HepG2 cell lines. | | Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1984 May;32(5):1872-7. | | Inhibitors of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Picrasma quassioides Bennet, and inhibitory activities of related .BETA.-carboline alkaloids.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) phosphodiesterase inhibitors present in Picrasma quassioides BENN. were identified as 1-methoxycarbonyl-β-carboline, 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one and 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one. The structure-inhibitory activity relationships were studied in 31 derivatives of β-carboline, 2 dimeric derivatives of β-carboline and 12 derivatives of canthin-6-one.
CONCLUSIONS:
β-Carboline derivatives with a methoxycarbonyl group and canthin-6-one derivatives with a methoxyl group generally had a strong inhibitory effect on cAMP phosphodiesterase. | | Yao Xue Xue Bao,1979, 14(3):167-77. | | Chemical investigation of the alkaloids of Ku-Mu [Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn.[Reference: WebLink] | Some preparation of the total alkaloids of Ku-Mu (Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn.) was Shown to have antibacterial actiyity in clinical trial. For the exploration of the active principles, the present paper deals with the studies of the alkaloids of this medicinal plant.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From an alcohol extract of heartwood of Ku-Mu seven alkaloids were isolated through silica gel and alumina column chromatography as well as preparative thin layer chromatography. Beside the known alkaloids 1-carbomethoxy-β-carboline (Ⅱ), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (Ⅳ), canthin-6-one (Ⅴ), and 4-methoxy-5-hydroxycanthin-6-one (Ⅵ), three new alkaloids, named Kumujian A, Kumujian G, and Kumujian G, were ident fied as 1-carboethoxy-β-carbotine (Ⅰ), 1-formyl-β-carboline(Ⅲ) and 1-vinyl-4,8-dimethoxy-β-carboline (Ⅶ), respectively. In vitro screening of the above alkaloids demonstrated that 1-carbomethoxy-β-carboline (Ⅱ), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (Ⅳ), 4-methoxy-5-hydroxycanthin-6-one (Ⅵ) and 1-vinyl-4,8-dimethoxy-β-carboline (Ⅶ) exhibited inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and its drug-resistant strains.
CONCLUSIONS:
Tests for the antibacterial activity of three other alkaloids were hampered by scarcity of material. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)