| In vitro: |
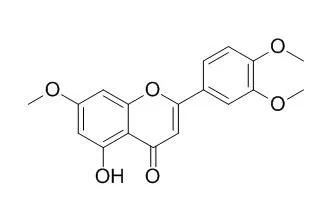
| Med. Chem. Res.,2016,25(9):1754-67. | | Protective effect of 5-hydroxy-3′,4′,7-trimethoxyflavone against inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide in RAW 264.7 macrophage: in vitro study and in silico validation.[Reference: WebLink] | The herb Lippia nodiflora L. (Verbenaceae) has been documented to exhibit anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antitussive, antidiabetic, anticancer, and antimelanogenesis properties. In the present study, we aimed at evaluating the anti-inflammatory activity of 5-Hydroxy-3',4',7-trimethoxyflavone, a flavonoid from L. nodiflora, using lipopolysaccharide induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
5-hydroxy-3′,4′,7-trimethoxyflavone significantly inhibited nitric oxide production and demonstrated slight reduction in prostaglandin-E2 level at tested concentrations. The production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, were obviously reduced by 5-Hydroxy-3',4',7-trimethoxyflavone in a concentration-dependent manner. Moreover, 5-Hydroxy-3',4',7-trimethoxyflavone significantly induced reduction in the mRNA expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2, representing that inhibition occurs at the transcriptional level. In addition, we performed molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulations to study the interaction of 5-Hydroxy-3',4',7-trimethoxyflavone with inflammatory mediators such as inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2. Docking study showed its hydrogen bond interactions with key residues in the active site of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2, enlightening its possible binding mode at the molecular level. The results of molecular dynamic simulations showed the stability of complexes and their interactions.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these findings envisage 5-Hydroxy-3',4',7-trimethoxyflavone as a potential candidate molecule for the progress of therapeutic strategy against inflammation-related diseases. | | Pharm. Biol.,2008, 41(7):483-6. | | Antifungal Flavonoids from Ballota glandulosissima.[Reference: WebLink] | The flavonoids kumatakenin (1), pachypodol (2), 5-Hydroxy-3',4',7-trimethoxyflavone (3), velutin (4), salvigenin (5), retusin (6) and corymbosin (7) have been isolated from the aerial parts of Ballota glandulosissima Hub.-Mor & Patzak. Among them, 2–4 and 7 have not been reported previously in the genus Ballota.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antibacterial and antifungal activities of 1–4 and 6 were tested against Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus faecalis, Echerichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, Candida krusei and Candida galabrata. | | J.Appl. Pharm. Sci.,2016,6(1):102-6. | | Anti-infective Activities of Secondary Metabolites from Vitex pinnata.[Reference: WebLink] | The phytochemical investigation of Vitex pinnata led to the isolation of a mixture of steroids β-sitosterol and stigmasterol (1a and 1b) and three known flavonoid identified as 5-Hydroxy-3',4',7-trimethoxyflavone(2), 5-hydroxy-7,4’-dimethoxy-flavone (3) and 5-hydroxy-3,3’,4’,7-tetramethoxyflavone (4). The structures of all isolated compounds were carried out by NMR and mass spectrometry.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The isolated compounds were evaluated for their anti-infective activities against Trypanosoma brucei brucei and Microbacterium marinum. Compound 1-4 showed moderate antitrypanosomal activity with MIC values of 6.25μg/ml, 19.0, 21.0 and 17.0μM, respectively while no activity observed on anti-mycobacterial.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study is the first to report the presence of three flavones and their antitrypanosomal activity from V. pinnata. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)