| Description: |
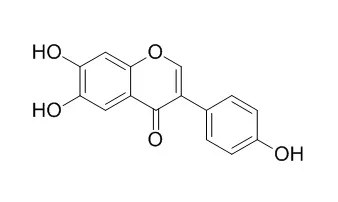
6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone, is a novel inhibitor of PKCα in suppressing solar UV-induced matrix metalloproteinase 1, which has antioxidant, and anti-cancer activities. 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone, suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes via ATP-competitive inhibition of PI3K. |
| Targets: |
ERK | MEK | JNK | p38MAPK | PKC | CDK | PI3K | ATP |
| In vitro: |
| Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Aug;57(8):1446-55. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201200593. Epub 2013 Jun 4. | | A metabolite of daidzein, 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone, suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes via ATP-competitive inhibition of PI3K.[Pubmed: 23737351] | Daidzein is one of the major soy isoflavones. Following ingestion, daidzein is readily metabolized in the liver and converted into hydroxylated metabolites. One such metabolite is 6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone (6,7,4'-THIF), which has been the focus of recent studies due to its various health benefits, however, its anti-adipogenic activity has not been investigated. Our objective was to determine the effects of 6,7,4'-THIF on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and elucidate the mechanisms of action involved.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Adipogenesis was stimulated in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Both 6,7,4'-THIF and daidzein were treated in the presence and absence of mixture of isobutylmethylxanthine, dexamethasone, and insulin (MDI). We observed that 6,7,4'-THIF, but not daidzein, inhibited MDI-induced adipogenesis significantly at 40 and 80 μM, associated with decreased peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ and C/EBP-α protein expression. 6,7,4'-THIF significantly suppressed MDI-induced lipid accumulation in the early stage of adipogenesis, attributable to a suppression of cell proliferation and the induction of cell cycle arrest. We also determined that 6,7,4'-THIF, but not daidzein, attenuated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. 6,7,4'-THIF was found to inhibit PI3K activity via direct binding in an ATP-competitive manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that 6,7,4'-THIF suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by directly targeting PI3K. Soy isoflavones like 6,7,4'-THIF may have potential for development into novel treatment strategies for chronic obesity. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Carcinogenesis. 2011 Apr;32(4):629-35. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr008. Epub 2011 Jan 21. | | 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone inhibits HCT-116 human colon cancer cell proliferation by targeting CDK1 and CDK2.[Pubmed: 21258042] | Colon cancer is a common epithelial malignancies worldwide. Epidemiologic evidence has shown that nutrition and dietary components are important environmental factors involved in the development of this disease.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the biological activity of 6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone (6,7,4'-THIF, a metabolite of daidzein) in in vitro and in vivo models of human colon cancer. 6,7,4'-THIF suppressed anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of HCT-116 and DLD1 human colon cancer cells more effectively than daidzein. In addition, 6,7,4'-THIF induced cell cycle arrest at the S and G2/M phases in HCT-116 human colon cancer cells. Western blot analysis revealed that 6,7,4'-THIF effectively suppressed the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 2, but had no effect on other S- or G2/M-phase regulatory proteins such as cyclin A, cyclin B1 or CDK1. Daidzein did not affect the expression of any of these proteins. In kinase and pull-down assays, 6,7,4'-THIF, but not daidzein, inhibited CDK1 and CDK2 activities in HCT-116 cells by directly interacting with CDK1 and CDK2. In a xenograft mouse model, 6,7,4'-THIF significantly decreased tumor growth, volume and weight of HCT-116 xenografts. 6,7,4'-THIF bound directly to CDK1 and CDK2 in vivo, resulting in the suppression of CDK1 and CDK2 activity in tumors corresponding with our in vitro results.
CONCLUSIONS:
Collectively, these results suggest that CDK1 and CDK2 are potential molecular targets of 6,7,4'-THIF to suppress HCT-116 cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. These findings provide insight into the biological actions of 6,7,4'-THIF and might establish a molecular basis for the development of new cancer therapeutic agents. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)