| Description: |
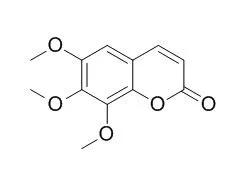
6,7,8-Trimethoxycoumarin has antiviral activity, it shows high anti-HRV-2 effect , with IC (50) value of 11.98 muM. It also can improve gastroprotective effects. |
| Targets: |
P450 (e.g. CYP17) | AChR | Antifection | HRV |
| In vitro: |
| Planta Med. 2009 Feb;75(3):195-204. | | In silico target fishing for rationalized ligand discovery exemplified on constituents of Ruta graveolens.[Pubmed: 19096995] | The identification of targets whose interaction is likely to result in the successful treatment of a disease is of growing interest for natural product scientists.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the current study we performed an exemplary application of a virtual parallel screening approach to identify potential targets for 16 secondary metabolites isolated and identified from the aerial parts of the medicinal plant RUTA GRAVEOLENS L. Low energy conformers of the isolated constituents were simultaneously screened against a set of 2208 pharmacophore models generated in-house for the IN SILICO prediction of putative biological targets, i. e., target fishing. Based on the predicted ligand-target interactions, we focused on three biological targets, namely acetylcholinesterase (AChE), the human rhinovirus (HRV) coat protein and the cannabinoid receptor type-2 (CB (2)). For a critical evaluation of the applied parallel screening approach, virtual hits and non-hits were assayed on the respective targets. For AChE the highest scoring virtual hit, arborinine, showed the best inhibitory IN VITRO activity on AChE (IC (50) 34.7 muM). Determination of the anti-HRV-2 effect revealed 6,7,8-Trimethoxycoumarin and arborinine to be the most active antiviral constituents with IC (50) values of 11.98 muM and 3.19 muM, respectively. Of these, arborinine was predicted virtually. Of all the molecules subjected to parallel screening, one virtual CB (2) ligand was obtained, i. e., rutamarin. Interestingly, in experimental studies only this compound showed a selective activity to the CB (2) receptor ( Ki of 7.4 muM) by using a radioligand displacement assay.
CONCLUSIONS:
The applied parallel screening paradigm with constituents of R. GRAVEOLENS on three different proteins has shown promise as an IN SILICO tool for rational target fishing and pharmacological profiling of extracts and single chemical entities in natural product research. | | J Ethnopharmacol. 1999 Dec 15;68(1-3):283-8. | | Antiviral flavonoid from Pterocaulon sphacelatum, an Australian Aboriginal medicine.[Pubmed: 10624889] | The antipicornaviral activity of an ethanolic extract of the green aerial parts of the Australian plant Pterocaulon sphacelatum (Labill.) Benth. & Hook. f. ex F. Muell. has been investigated. This plant has been a favoured traditional medicine, used for the treatment of colds by the Australian Aboriginal people.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antiviral activity-guided fractionation of the extract of P. sphacelatum using an inhibition of poliovirus-induced cytopathic effect assay, has yielded the antiviral flavonoid chrysosplenol C (3,7,3'-trimethoxy-5,6,4'-trihydroxyflavone). This compound is a 4'-hydroxy-3-methoxyflavone, one of a group of compounds known to be potent and specific inhibitors of picornaviral replication.
CONCLUSIONS:
These compounds inhibit the replication of rhinoviruses, the most frequent causative agent of the common cold. The coumarin 6,7,8-Trimethoxycoumarin was also isolated from the ethanolic extract. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Nutrients. 2015 Mar 13;7(3):1945-64. | | Gastroprotective efficacy and safety evaluation of scoparone derivatives on experimentally induced gastric lesions in rodents.[Pubmed: 25781220] | Among these compounds, 5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin and 6,7,8-Trimethoxycoumarin were found to have gastroprotective activity greater than the standard drug rebamipide; 6-methoxy-7,8-methylenedioxycoumarin, 6-methoxy-7,8-(1-methoxy)-methylenedioxycoumarin, 6,7-methylenedioxycoumarin, and 6,7-(1-methoxy)-methylenedioxycoumarin were found to be equipotent or less potent that of rebamipide. Pharmacological studies suggest that the presence of a methoxy group at position C-5 or C-8 of the scoparone's phenyl ring significantly improves gastroprotective activity, whereas the presence of a dioxolane ring at C-6, C-7, or C-8 was found to have decreased activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to assess toxicological safety, two of the potent gastroprotective scoparone derivatives-5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin and 6,7,8-Trimethoxycoumarin-were examined for their acute toxicity in mice as well as their effect on cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme activity. These two compounds showed low acute oral toxicity in adult male and female mice, and caused minimal changes to CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 enzyme activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that compared to other scoparone derivatives, 5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin and 6,7,8-Trimethoxycoumarin can improve gastroprotective effects, and they have low toxicity and minimal effects on drug-metabolizing enzymes. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)