| Structure Identification: |
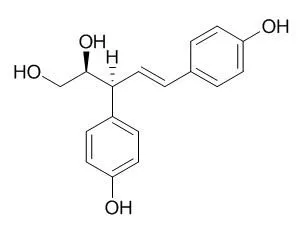
| J Plant Physiol. 2006 Mar;163(5):483-7. | | Evidence for involvement of the phenylpropanoid pathway in the biosynthesis of the norlignan agatharesinol.[Pubmed: 16473652] | In order to study the biosynthesis of Agatharesinol, a norlignan, l-phenylalanine-[ring-2,3,4,5,6-2H] and trans-cinnamic acid-[ring-13C6] were administered to fresh sapwood sticks of Cryptomeria japonica (sugi, Japanese cedar), that is, the labeled precursors were allowed to be absorbed through the tangential section of the wood sticks.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The wood sticks were then maintained in high humidity desiccators for approximately 20 d after which ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extracts of the wood sticks were analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Native Agatharesinol (trimethylsilylated) produces an m/z 369 ion and an m/z 484 ion that are characteristic of its structure. Agatharesinol formed in the sapwood sticks treated with the deuterium-labeled l-phenylalanine generated both of these ions together with m/z 373 and 377 ions (m/z 369+4 and +8, respectively), and also m/z 488 and 492 ions (m/z 484+4 and +8, respectively). Generation of m/z 373 and 488 ions is attributed to the substitution by deuterium of the four hydrogen atoms of either of the p-hydroxyphenyl rings of Agatharesinol, and that of m/z 377 and 492 ions is attributed to the substitution by deuterium of the eight hydrogen atoms of both p-hydroxyphenyl rings. In the administration of the 13C-labeled trans-cinnamic acid, m/z 375 and 381 ions (m/z 369+6 and +12, respectively), and also m/z 490 and 496 ions (m/z 484+6 and +12, respectively) were found, indicating that either aromatic ring or both aromatic rings of Agatharesinol were 13C-labeled.
CONCLUSIONS:
Consequently, assimilation of the labeled precursors into Agatharesinol was clearly detected, and an experimental procedure for studies on the biosynthesis was developed. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)