| Description: |
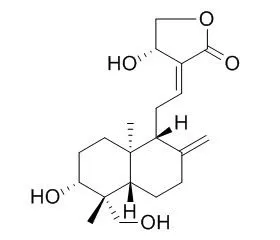
Andrographolide is an antiinflammatory, antiviral, anti-cancer , hepatoprotective, antithrombotic, hypotensive and antiatherosclerotic drug, it can cure hyperpigmentation disorders. Andrographolide protects against chemical-induced oxidative damage by up-regulating the gene transcription and activity of antioxidant enzymes in various tissues.Andrographolide has potential as a leading compound in the prevention or treatment of obesity and insulin resistance, can ameliorate lipid metabolism and improve glucose use in mice with HFD-induced obesity.
|
| In vitro: |
| J Dermatol Sci. 2015 Jul;79(1):74-83. | | Andrographolide suppresses melanin synthesis through Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin signal pathway.[Pubmed: 25869056] | Tyrosinase (TYR) is the key enzyme controlling the production of melanin. Very few papers have reported that Andrographolide can inhibit melanin content. To investigate the effects of Andrographolide on melanin synthesis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cell viability, melanin content, TYR activity, transcriptional and protein expression levels of TYR family and other kinds of proteins involved in melanogenesis were measured after the treatments of Andrographolide. It was found that Andrographolide decreased melanin content, TYR activity and transcriptional and protein expression of TYR family and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) in B16F10 melanoma cells. Data showed Andrographolide also decreased melanin content and TYR content in ultraviolet B (UVB) irradiation induced brown guinea pigs. Moreover, we found that melanin content and TYR activity were effectively inhibited in Human Epidermis Melanocyte (HEM) treated with Andrographolide at the medium concentrations without apparent effect on cell viability. Results in experiments treated with MG-132 or cycloheximide (CHX) showed that Andrographolide lowered the content of β-catenin in cell nucleus resulting from accelerating the degradation of β-catenin. Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) and Akt decreased simultaneously. 6-Bromoindirubin-3'-oxime (BIO, inhibitor of GSK3β) and insulin-like growth factors-1 (IGF-1, activator of Akt) could reverse the decline of β-catenin in B16F10 cells induced by Andrographolide.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrate that Andrographolide can effectively suppress melanin content and TYR activity in B16F10 cells, HEM cells and UVB-induced brown guinea pig skin by decreasing phosphorylation of GSK3β dependent on Akt, promoting the degradation of β-catenin, inhibiting β-catenin into the nucleus and decreasing the expression of MITF and TYR family. Data indicate that Andrographolide may be a potential whiting agent which can have great market in cosmetics and in clinical such as curing hyperpigmentation disorders. | | Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Apr 25;632(1-3):23-32. | | Inhibitory effects of andrographolide on migration and invasion in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells via down-regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 20097193 ] | Lung cancer is the leading cause of death among cancers worldwide and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) comprises more than 80% of lung cancer cases. Treatment options for patients with advanced NSCLC have evolved in the last decade with the advent of novel biological agents. Andrographolide, a diterpenoid lactone isolated from a traditional herbal medicine Andrographis paniculata, is known to have the potential to be developed as a chemotherapeutic agent.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to understand the anti-cancer properties of Andrographolide, we examined its effect on migration and invasion in human NSCLC A549 cells. The results of wound-healing assay and in vitro transwell assay revealed that Andrographolide inhibited dose-dependently the migration and invasion of A549 cells under non-cytotoxic concentrations. Molecular data showed that the effect of Andrographolide in A549 cells might be mediated via sustained inactivation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signal involved in the up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Our results showed that Andrographolide exerted an inhibitory effect on the activity and the mRNA and protein levels of MMP-7, but not MMP-2 or MMP-9. The Andrographolide-inhibited MMP-7 expression or activity appeared to occur via activator protein-1 (AP-1) because of its DNA binding activity was suppressed by Andrographolide. Additionally, the transfection of Akt over-expression vector (Akt1 cDNA) to A549 cells could result in an increase expression of MMP-7 concomitantly with a marked induction on cell invasion.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggested that the inhibition on MMP-7 expression by Andrographolide may be through suppression on PI3K/Akt/AP-1 signaling pathway, which in turn led to the reduced invasiveness of the cancer cells. | | J Ethnopharmacol. 1993 Oct;40(2):131-6. | | Andrographolide protects rat hepatocytes against paracetamol-induced damage.[Pubmed: 8133653] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Andrographolide, the active constituent isolated from the plant Andrographis paniculata, showed a significant dose dependent (0.75-12 mg/kg p.o. x 7) protective activity against paracetamol-induced toxicity on ex vivo preparation of isolated rat hepatocytes. It significantly increased the percent viability of the hepatocytes as tested by trypan blue exclusion and oxygen uptake tests. It completely antagonized the toxic effects of paracetamol on certain enzymes (GOT, GPT and alkaline phosphatase) in serum as well as in isolated hepatic cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Andrographolide was found to be more potent than silymarin, a standard hepatoprotective agent. | | Arch Virol . 2017 Mar;162(3):611-623. | | Broad-spectrum antiviral properties of andrographolide[Pubmed: 27896563] | | Abstract
Andrographolide, a diterpenoid, is known for its anti-inflammatory effects. It can be isolated from various plants of the genus Andrographis, commonly known as 'creat'. This purified compound has been tested for its anti-inflammatory effects in various stressful conditions, such as ischemia, pyrogenesis, arthritis, hepatic or neural toxicity, carcinoma, and oxidative stress, Apart from its anti-inflammatory effects, Andrographolide also exhibits immunomodulatory effects by effectively enhancing cytotoxic T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, phagocytosis, and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). All these properties of Andrographolide form the foundation for the use of this miraculous compound to restrain virus replication and virus-induced pathogenesis. The present article covers antiviral properties of Andrographolide in variety of viral infections, with the hope of developing of a new highly potent antiviral drug with multiple effects. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 1;280(1):1-9. | | Bioavailability of andrographolide and protection against carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative damage in rats.[Pubmed: 25110055] | Andrographolide, a bioactive diterpenoid, is identified in Andrographis paniculata. In this study, we investigated the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of Andrographolide in rats and studied whether Andrographolide enhances antioxidant defense in a variety of tissues and protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative damage.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After a single 50-mg/kg administration, the maximum plasma concentration of Andrographolide was 1μM which peaked at 30min. The bioavailability of Andrographolide was 1.19%. In a hepatoprotection study, rats were intragastrically dosed with 30 or 50mg/kg Andrographolide for 5 consecutive days. The results showed that Andrographolide up-regulated glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL) catalytic and modifier subunits, superoxide dismutase (SOD)-1, heme oxygenase (HO)-1, and glutathione (GSH) S-transferase (GST) Ya/Yb protein and mRNA expression in the liver, heart, and kidneys. The activity of SOD, GST, and GSH reductase was also increased in rats dosed with Andrographolide (p<0.05). Immunoblot analysis and EMSA revealed that Andrographolide increased nuclear Nrf2 contents and Nrf2 binding to DNA, respectively. After the 5-day Andrographolide treatment, one group of animals was intraperitoneally injected with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) at day 6. Andrographolide pretreatment suppressed CCl4-induced plasma aminotransferase activity and hepatic lipid peroxidation (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Andrographolide is quickly absorbed in the intestinal tract in rats with a bioavailability of 1.19%. Andrographolide protects against chemical-induced oxidative damage by up-regulating the gene transcription and activity of antioxidant enzymes in various tissues. | | Phytother Res. 2000 Aug;14(5):333-8. | | A phase I trial of andrographolide in HIV positive patients and normal volunteers.[Pubmed: 10925397] | A phase I dose-escalating clinical trial of Andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata was conducted in 13 HIV positive patients and five HIV uninfected, healthy volunteers.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The objectives were primarily to assess safety and tolerability and secondarily to assess effects on plasma virion HIV-1 RNA levels and CD4(+) lymphocyte levels. No subjects used antiretroviral medications during the trial. Those with liver or renal abnormalities were excluded. The planned regimen was 5 mg/kg bodyweight for 3 weeks, escalating to 10 mg/kg bodyweight for 3 weeks, and to 20 mg/kg bodyweight for a final 3 weeks. The trial was interrupted at 6 weeks due to adverse events including an anaphylactic reaction in one patient. All adverse events had resolved by the end of observation. A significant rise in the mean CD4(+) lymphocyte level of HIV subjects occurred after administration of 10 mg/kg Andrographolide (from a baseline of 405 cells/mm(3) to 501 cells/mm(3); p = 0.002). There were no statistically significant changes in mean plasma HIV-1 RNA levels throughout the trial. Andrographolide may inhibit HIV-induced cell cycle dysregulation, leading to a rise in CD4(+) lymphocyte levels in HIV-1 infected individuals. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)