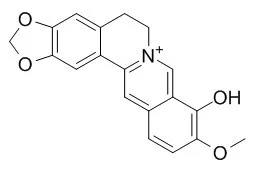
| Description: |
Berberrubine possesses diverse pharmacological activities, including glucose-lowering, lipid-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor effects. Berberrubine dose-dependently inhibits IL-8 and MCP-1 protein levels in the media and mRNA expression of the cells stimulated with IL-1beta or TNF-alpha. |
| Targets: |
LDL | IL Receptor | TNF-α | NF-kB | MCP-1 |
| In vitro: |
| Life Sci. 2006 Aug 1;79(10):949-56. | | Effect of berberrubine on interleukin-8 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cell line.[Pubmed: 16797033] | We examined the effects of Berberrubine, a protoberberine alkaloid, on interleukin-8 (IL-8) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) expression in a human retinal pigment epithelial cell line (ARPE-19) stimulated with interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) or tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha).
CONCLUSIONS:
ARPE-19 cells were cultured to confluence. Berberrubine and IL-1beta or TNF-alpha were added to the medium. IL-8 and MCP-1 protein concentrations were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. IL-8 and MCP-1 mRNA were measured by real time polymerase chain reaction. Nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) translocation was examined by immunofluorescent staining/microscopy. Berberrubine dose-dependently inhibited IL-8 and MCP-1 protein levels in the media and mRNA expression of the cells stimulated with IL-1beta or TNF-alpha. Immunofluorescent staining/microscopy of NF-kappaB in the nucleus of unstimulated cells was faint (51+/-14 arbitrary units). Fluorescein was dense (215+/-42 or 170+/-24 arbitrary units, respectively) 30 min after stimulation with IL-1beta or TNF-alpha and was decreased to 62+/-18 or 47+/-16 arbitrary units, respectively, by Berberrubine.
CONCLUSIONS:
Berberrubine dose-dependently inhibited IL-8 and MCP-1 expression and protein secretion induced by IL-1beta or TNF-alpha. Possibly, the effect on chemotactic factors may be via suppression of NF-kappaB translocation. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Sep 1;18(17):6422-8. | | Design, synthesis, and cholesterol-lowering efficacy for prodrugs of berberrubine.[Pubmed: 20673726] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to enhance oral bioavailability of berberine (BBR) for its cholesterol-lowering efficacy in vivo, a series of ester or ether prodrugs of Berberrubine (M1), which is an active metabolite of BBR after first-pass metabolism, were designed, semi-synthesized, and evaluated. Among these Berberrubine prodrugs, compound 5g possessing palmitate at the 9-position showed a moderate LogP value and esterase hydrolysis rate for releasing Berberrubine in blood. Its cholesterol-lowering efficacy in vivo was evaluated in hyperlipidemic SD rats. Compound 5g (100mg/kg/d) reduced blood CHO and LDL-c by 35.8% and 45.5%, respectively, similar to that by BBR. It also exhibited a good safety in rats with no side-effect on liver and kidney function.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, the design of Berberrubine prodrug appears to be an effective strategy to improve pharmacokinetic feature of BBR for its lipid-lowering efficacy in vivo. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)