| Structure Identification: |
| J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 Jan 5;132:148-155. | | Dereplication-guided isolation of novel hepatoprotective triterpenoid saponins from Celosiae Semen by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 27721071 ] | Although natural products (NPs) from ethnomedical plants have played a vital role in modern drug discovery, separation and purification of bioactive compounds from plant extract is still challenging.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, a dereplication strategy using HPLC-QTOF-MS was employed to rapidly discover and highly targeted isolate the novel hepatoprotective triterpenoid saponins from the methanol extract of Celosiae Semen. Firstly, four known saponins, i.e. celosin H, celosin I, Celosin J, and pseudoginsenoside RT1 were selected as model compounds, and their fragmentation patterns in ESI-QTOF-MS/MS were characterized. Secondly, an HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS method was applied to chemically screen the saponins of interest, and thereby to guide the subsequent fraction and isolation procedure. Thirdly, the targeted isolation of desired compounds afforded two new triterpenoid saponins namely celosin K (1) and celosin L (2), which were structurally elucidated by combination of extensive NMR spectroscopic and chemical analyses. Finally, the protective effects of compounds 1 and 2 against APAP-induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cells were evaluated.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that the HPLC-QTOF-MS-guided isolation is an efficient methodology for isolating new NPs from medicinal plants through improving selectivity in separation and purification process. | | J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2014;16(3):240-7. | | New oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins isolated from the seeds of Celosia argentea.[Pubmed: 24456247 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
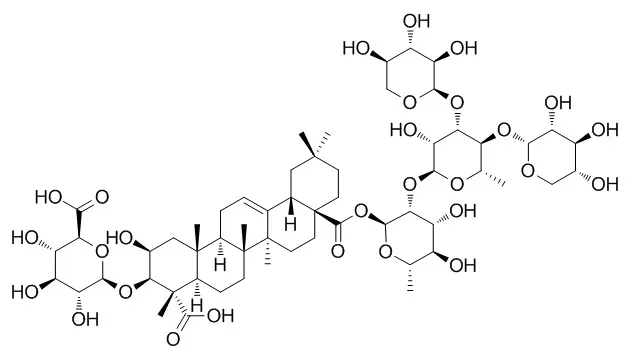
Three new oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins named celosins H, I, and J were isolated from the seeds of Celosia argentea L. Their structures were characterized as 3-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1 → 3)-β-D-glucuronopyranosyl-polygalagenin 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester, 3-O-β-D-glucuronopyranosyl-medicagenic acid 28-O-β-D-xylcopyranosyl-(1 → 4)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 → 2)-β-D-fucopyranosyl ester, and 3-O-β-D-glucuronopyranosyl-medicagenic acid 28-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1 → 3)-[β-D-xylcopyranosyl-(1 → 4)]-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 → 2)-β-D-fucopyranosyl ester by NMR, MS, and chemical evidences, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
In our opinion, celosin H, celosin I, Celosin J could be used as chemical markers for the quality control of C. argentea seeds. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)