| In vitro: |
| Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Mar 9. | | Functional Characterization of Cucurbitadienol Synthase and Triterpene Glycosyltransferase Involved in Biosynthesis of Mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii.[Pubmed: 25759326] | Hexahydrocurcumin, 1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione, 6-dehydroshogaol and 6-shogaol were evaluated for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in the present study.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The relative antioxidant potencies of ginger compounds decreased in similar order of 1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione, hexahydrocurcumin>6-shogaol>6-dehydroshogaol in both 1,1-diphenyl-2-picyrlhydrazyl (DPPH) radical-scavenging and trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assays. All tested compounds could attenuate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-elicited increase of prostaglandin E2 (PGE(2)) in murine macrophages (RAW 264.7) in a concentration-dependent manner but hexahydrocurcumin of 7μM and 6-shogaol of 7μM. The strongest inhibitory effect was observed for 6-dehydroshogaol and 6-shogaol at 14μM with the inhibition of 53.3% and 48.9%, respectively. Furthermore, both 6-dehydroshogaol and 1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione significantly suppressed the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) proteins in a concentration-dependent fashion.
CONCLUSIONS:
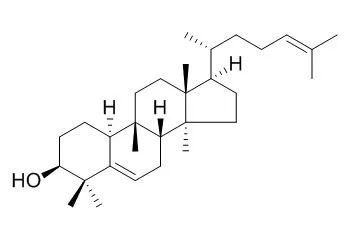
These results contribute to our theoretical understanding of the potential beneficial effects of consuming ginger as a food and/or dietary supplement. | | Plant Cell Physiol., 2016,57(5):1000-7. | | Oxidation of Cucurbitadienol Catalyzed by CYP87D18 in the Biosynthesis of Mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii.[Pubmed: 26903528 ] | Mogrosides, the principally bioactive compounds extracted from the fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii, are a group of glycosylated cucurbitane-type tetracyclic triterpenoid saponins that exhibit a wide range of notable biological activities and are commercially available worldwide as natural sweeteners.
The biosynthesis of mogrosides involves initial cyclization of 2,3-oxidosqualene to the triterpenoid skeleton of Cucurbitadienol, followed by a series of oxidation reactions catalyzed by Cyt P450s (P450s) and then glycosylation reactions catalyzed by UDP glycosyltransferases (UGTs). We previously reported the identification of a Cucurbitadienol synthase (SgCbQ) and a mogrol C-3 hydroxyl glycosyltransferase (UGT74AC1). However, molecular characterization of further transformation of Cucurbitadienol to mogrol by P450s remains unavailable.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we report the successful identification of a multifunctional P450 (CYP87D18) as being involved in C-11 oxidation of Cucurbitadienol. In vitro enzymatic activity assays showed that CYP87D18 catalyzed the oxidation of Cucurbitadienol at C-11 to produce 11-oxo Cucurbitadienol and 11-hydroxy Cucurbitadienol. Furthermore, 11-oxo-24,25-epoxy Cucurbitadienol as well as 11-oxo Cucurbitadienol and 11-hydroxy Cucurbitadienol were produced when CYP87D18 was co-expressed with SgCbQ in genetic yeast, and their structures were confirmed by liquid chromatography-solid-phase extraction-nuclear magnetic resonance-mass spectrometry coupling (LC-SPE-NMR-MS).
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggest a role for CYP87D18 as a multifunctional Cucurbitadienol oxidase in the mogrosides pathway. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)