| Structure Identification: |
| J Bacteriol. 2012 Apr;194(8):1868-74. | | Biochemical characterization of the CDP-D-arabinitol biosynthetic pathway in Streptococcus pneumoniae 17F.[Pubmed: 22328666 ] | The biosynthetic pathway of D-arabinitol, which is present in the CPSs of several S. pneumoniae serotypes, has never been identified.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the genes abpA (previously known as abp1) and abpB (previously known as abp2), which have previously been reported to be responsible for nucleoside diphosphate (NDP)-D-arabinitol (the nucleotide-activated form of D-arabinitol) synthesis, were cloned. As a result, abpA was identified to be a D-xylulose-5-phosphate cytidylyltransferase-encoding gene, responsible for the transfer of CTP to D-xylulose-5-phosphate (D-Xlu-5-P) to form CDP-D-xylulose, and abpB was characterized to be a CDP-D-xylulose reductase-encoding gene, responsible for the conversion of CDP-D-xylulose to CDP-D-arabinitol as the final product. The kinetic parameters of AbpA for the substrates D-Xlu-5-P and CTP and those of AbpB for the substrate CDP-D-xylulose and the cofactors NADH or NADPH were measured, and the effects of temperature, pH, and cations on the two enzymes were analyzed.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study confirmed the involvement of the genes abpA and abpB and their products in the biosynthetic pathway of CDP-D-arabinitol. |
|


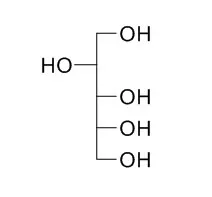



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)