| In vitro: |
| Vet Parasitol. 2008 Dec 20;158(4):288-94. | | In vitro antitrypanosomal activities of quassinoid compounds from the fruits of a medicinal plant, Brucea javanica.[Pubmed: 18986767] | The medicinal plant Brucea javanica (L.) Merr. (Simaroubaceae) is widely distributed throughout Asia where its bitter fruits have been used in traditional medicine for various ailments.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
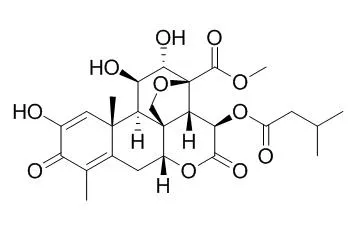
Fifteen C-20 quassinoids were isolated from the fruits of B. javanica and examined for their in vitro antitrypanosomal activities against trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma evansi. Bruceine A, bruceantinol, bruceine C, brusatol, and bruceine B showed strong antitrypanosomal activities with IC(50) values in the range of 2.9-17.8nM, which compared well with the standard trypanocidal drugs diminazene aceturate (IC(50)=8.8nM) and suramin (IC(50)=43.2nM). However, Dehydrobruceine A, dehydrobruceine B, and dehydrobrusatol were about 2100, 900, and 1200 times less active, respectively, than bruceine A, bruceine B, and brusatol.
CONCLUSIONS:
The relationship of the structure and antitrypanosomal activity of these quassinoid compounds suggested that the presence of a diosphenol moiety in ring A and the nature of the C-15 side chain are important for their activities against T. evansi. This is the first report on the antitrypanosomal activity of isolated quassinoids. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)