| Kinase Assay: |
| The HKU Scholars Hub, 2016. | | Postgraduate Thesis: Study on the therapeutic effect of dendrobine from dendrobium officinale on non-small cell lung carcinoma.[Reference: WebLink] | Lung cancer is the major cause of cancer deaths around the world, including about 15% of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and approximately 85% non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Although clinical outcomes of early-stages of lung cancer have made great progress by advancements in surgery, chemo or radiotherapy and development of molecular targeted therapy, toxicity limits their anticancer efficancy. Chinese medicine with the merits of multi-targets, low toxicity and low risk of drug resistance, has been widely applied for lung cancer treatment in China. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has well established theoretical system, large amount of case reports, thousands years history, TCM still confront much negative, pessimism and skepticism due to lack of laboratory evidences and quality assurance.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, I aim to screen bioactive compounds in an herb Dendrobium nobile (D. nobile) on the treatment of NSCLC. Apoptosis as a crucial mechanism involved in lung cancer therapy has been studied. Annexin V/PI staining was applied to detect whether bioactive compounds of D. nobile could trigger apoptosis in NSCLC A549 cells. Our results demonstrated that Dendrobine inhibited the growth of A549 cells through inducing apoptosis, which was partially dependent on mitochondrial-mediated pathway. Dendrobine treatment decreased mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), improved the expression of Bax and inhibited the expression of Bcl-2, therefore it was supposed that Dendrobine treatment decreased the MMP through regulating the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax. Dendrobine released cytochrome c and promoted caspase 9 activation indicating that Dendrobine-induced apoptosis is partially caspase-dependent. In TCM theory, blood stasis and Qi stagnation partly result in cancer formation, which is correlated to tumor microenvironment. Tumor spread and metastasis are closely related to tumor cell water permeability and aquaporin 5 (AQP5) expression. Consequently, the therapeutic role of AQP5 on lung cancer treatment was evaluated. AQP5 expression was found to be correlated with lung cancer size. AQP5 silencing in the lung cancer resulted in an inhibition of A549 cells, mitochondrial pathway apoptosis and limited tumorigenic ability. AQP5 inhibition provided a promising therapeutic and preventive strategy for NSCLC. In clinic, in order to avoid unacceptable side effects of the drugs, two or more drugs are usually combined applied to increase therapeutic efficacy while. In this regard, the combination of Dendrobine and cisplatin on the treatment in NSCLC were studied. The combination treatment of cisplatin and Dendrobine displayed enhanced cancer-inhibition toxicity without aggravating more side effects. This study provided a valuable strategy to perfect the anticancer activity of commonly used chemotherapy drugs. Drug combination treatment can make out the full ability of the anticancer efficacy of anticancer drugs and enlarge the using of the drugs to many kinds of cancer types.
CONCLUSIONS:
In this study, preliminary laboratory evidences for applying Dendrobine in lung cancer therapy has been provided. However, its metabolism, synergistic effects with chemodrug and clinical efficacy is needed in further research. |
|


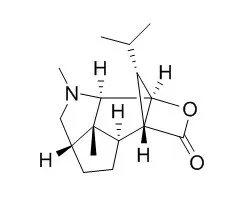



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)