| In vitro: |
| Industrial Crops & Products,2015, 76(1):653-9. | | Phytochemical and phytotoxic investigation of the flowers from Citharexylum spinosum L.[Reference: WebLink] | The aim of this study was to assess the phytotoxic potential of flowers of Citharexylum spinosum, as well as to isolate the main bioactive compounds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
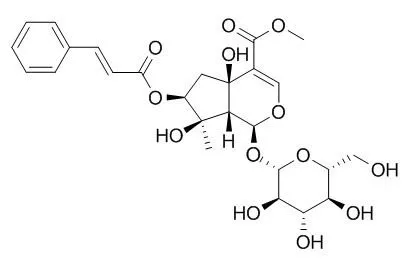
Results showed that the ethyl acetate extract induced the highest reduction, showing 100% inhibition of lettuce growth at 6000 ppm. This bioactive ethyl acetate extract was subjected to bio-guided chromatographic separation yielding the acetylated form of a new iridoid glucoside, designated as spinoside (1) together with two acetylated forms (2a) and (2b) of its known analogue Durantoside I (2).
CONCLUSIONS:
Their structures were established via their acetylated derivatives by means of spectroscopic and chemical data. The most inhibitory compound on the growth of lettuce seedling was identified to be the durantoside-I tetraacetylated (2b). | | J. Pharm. Res.,2013,7(2):162-6. | | New protein glycation inhibitory free radical scavenging compound from Duranta repens L.[Reference: WebLink] | Hyperglycemia induced oxidative stress, increased generation of free radicals and free radicals mediated glycation of protein molecules are important events aggravating development of a number of diabetic complications.
To identify antiglycation principles with free radicals scavenging activities from traditional oriental medicinal plants.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Biological activity ABTS+ radical scavenging in particular, guided isolation of active compounds was performed from methanolic extract of traditional oriental medicinal plants Duranta repense. Isolated compounds were further studied for their DPPH radical scavenging activity and advanced glycation end-products inhibitory potentials in vitro.
Activity guided isolation from methanolic extract of D. repens led to the identification of five iridoids namely Caryoptoside (1), Duraterectoside A (2), Durantoside III (3), Durantoside I (4), Lamiide (7) and two lignans namely (+) 5′Methoxyisolariciresinol (5), (−)5′Methoxyisolariciresinol (6). All the compounds scavenged ABTS+ radical, Caryoptoside (1) and (+) 5′Methoxyisolariciresinol (5) being most potent ABTS+ scavenger (IC50 = 6.0 and 3.1 μg/mL respectively). Only (+) 5′Methoxyisolariciresinol (5) displayed DPPH scavenging activity (IC50 = 70.5 μg/mL). Despite being potent ABTS+ scavenges, iridoid compounds rather augmented glucose induced formation of advanced glycation end-products in bovine serum albumin protein. (+) 5′Methoxyisolariciresinol (5) displayed both, the potent ABTS+ and DPPH scavenging activity however, showed mild (10%) antiglycation activity. On the other hand, (−) isomer of lignin 5′Methoxyisolariciresinol (6) that displayed moderate ABTS+ scavenging activity (IC50 = 42.6 μg/mL) potently inhibited (45%) glucose induced glycation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) protein.
CONCLUSIONS:
Methanol extract of D. repense possess potent antioxidant compounds. Iridoids augmented glucose induced glycation of BSA. Lignans displayed antiglycation activity. The (−) isomer of lignan 5′Methoxyisolariciresinol (6) was five times more potent in inhibiting glucose induced generation of AGEs in BSA. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)