| In vitro: |
| Nat Prod Commun. 2010 Aug;5(8):1225-32. | | Phenolic compounds in leaves of Alchornea triplinervia: anatomical localization, mutagenicity, and antibacterial activity.[Pubmed: 20839624] | Phenolic compounds are produced by secretory idioblasts and hypodermis, and by specialized cells of the epidermis and chlorenchyma of leaves of Alchornea triplinervia.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
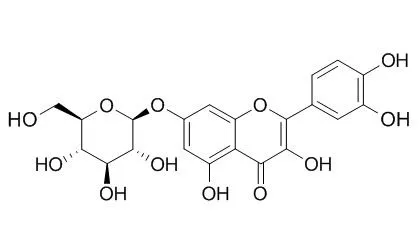
Phytochemical investigation of these leaves led to the isolation of the known substances quercetin, Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, quercetin-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside, quercetin-3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside, amentoflavone, brevifolin carboxylic acid, gallic acid, and methyl gallate from the methanolic extract, and stigmasterol, campesterol, sitosterol, lupeol, friedelan-3-ol, and friedelan-3-one from the chloroform extract.
CONCLUSIONS:
In studies of antibacterial activity and mutagenicity, the methanolic extract showed promising activity against Staphylococcus aureus (MIC = 62.5 microg/mL) and was slightly mutagenic in vitro and in vivo at the highest concentrations tested (1335 mg/kg b.w.). | | J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1127-34. | | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of quercetin 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from the leaves of Brasenia schreberi.[Pubmed: 21859349] | Brasenia schreberi Gmel. (Cabombaceae) is an aquatic plant that grows in eastern Asia, Australia, Africa, and North and Central America. B. schreberi leaf extracts were obtained by sequential solvent extraction with dichloromethane, methanol, and water. The antioxidant potential of each extract was assessed by using the oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) assay.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
With this method, methanol and water extracts were found to be active with mean ± standard deviation values of 7 ± 2 and 5.1 ± 0.5 μmol Trolox® equivalents (TE)/mg, respectively. Two major phenolic compounds, Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside and gallic acid, were respectively isolated from the methanolic and water extracts. Both compounds exhibited antioxidant activities, in particular quercetin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (ORAC value, 18 ± 4 μmol TE/μmol). In contrast to its well-known antioxidant homologue quercetin, Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside does not inhibit growth of human fibroblasts (WS-1) or murine macrophages (RAW 264.7). Some flavonoids have been reported to possess beneficial effects in cardiovascular and chronic inflammatory diseases associated with overproduction of nitric oxide.
CONCLUSIONS:
Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside possesses anti-inflammatory activity, inhibiting expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and release of nitric oxide by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages in a dose-dependent manner. Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside also inhibited overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 and granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor. | | Arch Pharm Res. 2002 Jun;25(3):313-9. | | Antioxidative flavonoids from leaves of Carthamus tinctorius.[Pubmed: 12135103] | A total of eight flavonoids (1-8), including a novel quercetin-7-O-(6''-O-acetyl)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (6) and seven known flavonoids, luteolin (1), quercetin (2), luteolin 7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), luteolin-7-O-(6''-O-acetyl)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (4) Quercetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (5), acacetin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide (7) and apigenin-6-C-beta-D-glucopyrano syl-8-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside (8), have been isolated from the leaves of the safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) and identified on the basis of spectroscopic and chemical studies.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antioxidative activity of these flavonoids was evaluated against 2-deoxyribose degradation and rat liver microsomal lipid peroxidation induced by hydroxyl radicals generated via a Fenton-type reaction. Among these flavonoids, luteolin-acetyl-glucoside (4) and quercetin-acetyl-glucoside (6) showed potent antioxidative activities against 2-deoxyribose degradation and lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes. Luteolin (1), quercetin (2), and their corresponding glycosides (3 & 5) also exhibited strong antioxidative activity, while acacetin glucuronide (7) and apigenin-6,8-di-C-glucoside (8) were relatively less active. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)