| Kinase Assay: |
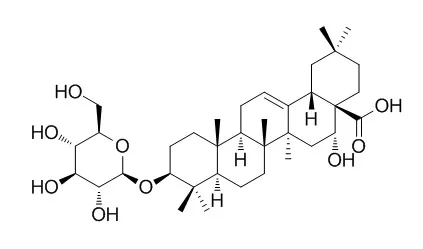
| Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 27 Feb 2016, 132(1):6-14. | | Eclalbasaponin II induces autophagic and apoptotic cell death in human ovarian cancer cells.[Reference: WebLink] | Triterpenoids echinocystic acid and its glycosides, isolated from several Eclipta prostrata, have been reported to possess various biological activities such as anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, and anti-diabetic activity. However, the cytotoxicity of the triterpenoids in human cancer cells and their molecular mechanism of action are poorly understood.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we found that Eclalbasaponin II with one glucose moiety has potent cytotoxicity in three ovarian cancer cells and two endometrial cancer cells compared to an aglycone echinocystic acid and eclalbasaponin I with two glucose moiety. Eclalbasaponin II treatment dose-dependently increased sub G1 population. Annexin V staining revealed that Eclalbasaponin II induced apoptosis in SKOV3 and A2780 ovarian cancer cells. In addition, Eclalbasaponin II-induced cell death was associated with characteristics of autophagy; an increase in acidic vesicular organelle content and elevation of the levels of LC3-II. Interestingly, autophagy inhibitor BaF1 suppressed the Eclalbasaponin II-induced apoptosis. Moreover, Eclalbasaponin II activated JNK and p38 signaling and inhibited the mTOR signaling. We further demonstrated that pre-treatment with a JNK and p38 inhibitor and mTOR activator attenuated the Eclalbasaponin II-induced autophagy.
CONCLUSIONS:
This suggests that Eclalbasaponin II induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death through the regulation of JNK, p38, and mTOR signaling in human ovarian cancer cells. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Neurochemical Research, 21 Nov 2017, 43(2):351-362. | | Eclalbasaponin II Ameliorates the Cognitive Impairment Induced by Cholinergic Blockade in Mice.[Reference: WebLink] | Eclalbasaponin II derived from Eclipta prostrata L. (Asteraceae) has been reported to have anti-fibrotic, anti-bacterial and autophagic activities, but its effect on cognitive function has not been investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We studied the effect of Eclalbasaponin II on cholinergic blockade-induced memory impairment in mice using the passive avoidance, Y-maze, and Morris water maze tasks. Eclalbasaponin II (10 or 20 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly ameliorated the cognitive dysfunction induced by scopolamine in the passive avoidance, Y-maze, and the Morris water maze tasks. To identify the mechanism of the memory-ameliorating effect of Eclalbasaponin II, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity assay, Western blot analysis and electrophysiology were conducted. Eclalbasaponin II inhibited the AChE activity in ex vivo study, and the administration of Eclalbasaponin II and its metabolite, echinocystic acid, increased the phosphorylation levels of memory-related signaling molecules, including protein kinase B (Akt) and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), in the hippocampus. Although Eclalbasaponin II did not affect hippocampal long term potentiation (LTP), echinocystic acid significantly enhanced hippocampal LTP formation (30 μM).
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Eclalbasaponin II ameliorates cholinergic blockade-induced cognitive impairment via AChE inhibition, LTP formation and the activation of Akt-GSK-3β signaling, and that Eclalbasaponin II may be a useful to treat cognitive impairment derived from cholinergic dysfunction. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| Phytochemistry Letters, 2016, 15:210-214. | | NF-κB inhibitory activities of triterpenoid glycosides from the stems of Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Harms.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three new triterpenoid glycosides, 3β-hydroxy-28-norolean-12-ene-16-one 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (1), 3β,17β-dihydroxy-28-norolean-12-ene-16-one 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (2) and 3β-hydroxy-olean-12-ene-16,28-lactone 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (3) together with Eclalbasaponin II (4) were isolated from Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Harms. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic and physico-chemical analyses. Inhibition of NF-κB of these isolates was measured in HepG2 cells using a luciferase reporter system.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among the isolates, compounds 1, 2 and 4 inhibited NF-κB activation stimulated by TNF-α in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50 values ranging from 8.3 ± 0.7 to 13.5 ± 1.0 μM. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)