| Description: |
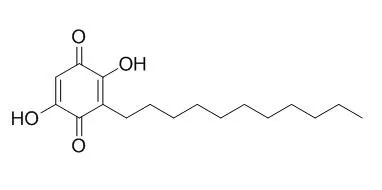
Embelin is an inhibitor of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) with IC50 of 4.1 μM in a cell-free assay.Embelin has antitumor, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Embelin can enhance TRAIL-induced cell apoptosis through DR4 and DR5 upregulation and decrease IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation, that combination of low-toxicity Embelin and TRAIL may become as a potential antileukemia strategy. |
| Targets: |
STAT | p53 | IL Receptor | gp120/CD4 | NF-kB | TNF-α | VEGFR | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | XIAP | DR4 | DR5 |
| In vitro: |
| Tumour Biol. 2015 Feb;36(2):769-77. | | The XIAP inhibitor Embelin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells by DR4 and DR5 upregulation.[Pubmed: 25293521] | The present study was designed to explore the effects of low-toxicity Embelin on TRAIL-induced apoptosis and its possible mechanism in human leukemia cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Our study showed that low-toxicity Embelin enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis through DR4 and DR5 upregulation and caspase activation in HL-60 cells. Pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK inhibited cell apoptosis induced by TRAIL alone or combined with low-toxicity Embelin, which indicated the cytotoxic effect is mediated by caspase-dependent apoptosis. Although Embelin is an X chromosome-linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein (XIAP) inhibitor, an XIAP independent effect on cell death was detected in HL-60 cells exposed to low-toxicity Embelin and TRAIL. Low-toxicity Embelin upregulated DR4 and DR5 expression to enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis. The sensitizing effects of Embelin on TRAIL-induced apoptosis were markedly attenuated when DR4/DR5 was knocked down.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggested that low-toxicity Embelin enhanced TRAIL-induced cell apoptosis through DR4 and DR5 upregulation, indicating that combination of low-toxicity Embelin and TRAIL may become as a potential antileukemia strategy. | | BMC Cancer. 2014 Oct 22;14:775. | | Embelin inhibits TNF-α converting enzyme and cancer cell metastasis: molecular dynamics and experimental evidence.[Pubmed: 25336399] | Embelin, a quinone derivative, is found in the fruits of Embelia ribes Burm (Myrsinaceae). It has been shown to have a variety of therapeutic potentials including anthelmintic, anti-tumor, anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial and anti-inflammation. Several studies have shown that the anti-inflammatory activity of Embelin is mediated by reduction in TNF-α. The latter is synthesized as a membrane anchored protein (pro-TNF-α); the soluble component of pro-TNF-α is then released into the extracellular space by the action of a protease called TNF-α converting enzyme (TACE). TACE, hence, has been proposed as a therapeutic target for inflammation and cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We used molecular docking and experimental approaches to investigate the docking potential and molecular effects of Embelin to TACE and human cancer cell characteristics, respectively. We demonstrate that Embelin is a potential inhibitor of TACE. Furthermore, in vitro studies revealed that it inhibits malignant properties of cancer cells through inactivation of metastatic signaling molecules including MMPs, VEGF and hnRNP-K in breast cancer cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on the molecular dynamics and experimental data, Embelin is proposed as a natural anti-inflammatory and anticancer drug. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 May;13(5):1206-16. | | Embelin reduces colitis-associated tumorigenesis through limiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling.[Pubmed: 24651526] | Embelin is a small molecule inhibitor of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor activities. We previously showed that Embelin inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells in vitro, and effectively suppresses 1,2-dimethylhydrazine dihydrochloride-induced colon carcinogenesis in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we explored the antitumor effects and mechanisms of Embelin on colitis-associated cancer (CAC) using the azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium (AOM/DSS) model, with a particular focus on whether Embelin exerts its effect through the IL-6/STAT3 pathway. We found that Embelin significantly reduced incidence and tumor size in CAC-bearing mice. In addition to inhibiting proliferation of tumor epithelial cells, Embelin suppressed colonic IL-6 expression and secretion, and subsequently STAT3 activation in vivo. Importantly, in vitro studies have revealed that in colon cancer cells, Embelin diminished both the constitutive and IL-6-induced STAT3 activation by stimulating Src homology domain 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP2) activity. Moreover, Embelin protected mice from AOM/DSS-induced colitis before tumor development. Embelin decreased IL-1β, IL-17a, and IL-23a expression as well as the number of CD4(+) T cells and macrophages infiltrating the colonic tissues.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, our findings demonstrated that Embelin suppresses CAC tumorigenesis, and its antitumor effect is partly mediated by limiting IL-6/STAT3 activation and Th17 immune response. Embelin may be a potential agent in the prevention and treatment of CAC. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)