| Description: |
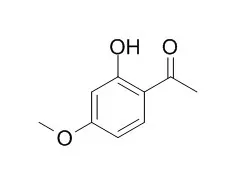
Paeonol has anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and cardiovascular protective activities, it shows a novel inhibitory role on neuroinflammation, and presents a new candidate agent for the development of therapies for inflammation-related neurodegenerative diseases. Paeonol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokines in macrophage cells and protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock. Paeonol inhibits MAO-A and MAO-B with IC50 of 54.6 μM and 42.5 μM, respectively; it inhibits PGE₂ synthesis and COX-2 expression, and modulates Sirtuin 1, PKCδ and c-Src signaling pathway. |
| In vitro: |
| J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Jun 11;154(2):428-36. | | Paeonol protects against premature senescence in endothelial cells by modulating Sirtuin 1 pathway.[Pubmed: 24768807] | Paeonol is a phenolic compound isolated mainly from Moutan cortex, root bark of Chinese Peony tree. Moutan cortex holds a significant value in traditional Chinese medicine for alleviating various oxidative stress-related diseases mainly atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction. The present study seeks to identify the protective mechanisms of Paeonol in oxidative stress-induced premature senescence in endothelial cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
HUVECs were pretreated with Paeonol or DMSO control at different doses for 24h prior to an exposure of 200μM of reactive oxygen species (ROS) inducer, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The protective effects of Paeonol against H2O2-induced senescence were evaluated and the activation of Sirtuin 1 pathway by Paeonol pretreatment was investigated in HUVECs.
Paeonol attenuated H2O2-induced cell growth arrest at G0/G1 phase, reduced the percentage of SA-β-Gal positive cells and increased BrdU incorporation. In addition, enzymatic Sirt1 activation assay indicated that Paeonol significantly increased lysyl deactylase activity of Sirt1 enzyme with a fold change of 2.4±0.195 (p<0.05). Furthermore, pretreatment with Paeonol significantly decreased the levels of p53, acetyl H3K14 and H4K16 protein expression upregulated by H2O2 stimulation. The changes in the histone protein levels were accompanied with an increase in Sirt1 protein expression level.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that Paeonol protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress-induced premature senescence by modulating the expressions of Sirt1 protein and its substrates. | | Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jul 2;15(7):11760-72. | | Paeonol suppresses chondrosarcoma metastasis through up-regulation of miR-141 by modulating PKCδ and c-Src signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 24992595] | Chondrosarcoma, a primary malignant bone cancer, has potential for local invasion and distant metastasis, especially to the lungs. Patients diagnosed with it show poor prognosis. Paeonol (2'-hydroxy-4'-methoxyacetophenone), the main active compound of traditional Chinese remedy Paeonia lactiflora Pallas, exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor activity; whether Paeonol regulates metastatic chondrosarcoma is largely unknown.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we find Paeonol do not increase apoptosis. By contrast, at non-cytotoxic concentrations, Paeonol suppresses migration and invasion of chondrosarcoma cells. We also demonstrate Paeonol enhancing miR-141 expression and miR-141 inhibitor reversing Paeonol-inhibited cell motility; Paeonol also reduces protein kinase C (PKC)d and c-Src kinase activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Since Paeonol inhibits migration and invasion of human chondrosarcoma via up-regulation of miR-141 via PKCd and c-Src pathways, it thus might be a novel anti-metastasis agent for treatment of metastatic chondrosarcoma. | | Int Immunopharmacol. 2007 Mar;7(3):343-50. | | Paeonol suppresses intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells by blocking p38, ERK and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 17276892 ] | Paeonol (2'-hydroxy-4'-methoxyacetophenone), the main active compound of the traditionally used Chinese herb Paeonia lactiflora Pallas, has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and cardiovascular protective activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We studied how the levels of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), one of the key molecules in the development of atherosclerosis, might be affected by Paeonol in tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Paeonol concentration-dependently inhibited the production of ICAM-1; it inhibited nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) p65 translocation into the nucleus and the phosphorylation of inhibitory factor kappaBalpha (IkappaBalpha). It also blocked the TNF-alpha-induced phosphorylation of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), which are involved in regulating ICAM-1 production by TNF-alpha. Paeonol inhibited U937 monocyte adhesion to HUVECs stimulated by TNF-alpha, suggesting that it may inhibit the binding of monocytes to endothelium by regulating the production of critical adhesion molecules by TNF-alpha. The inhibitory effect of Paeonol on ICAM-1 production might be mediated by inhibiting p38, ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways, which are involved in TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 production.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, Paeonol may be beneficial in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders such as atherosclerosis. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)