| In vitro: |
| J Nat Med. 2016 Apr;70(2):290-5. | | Two new prenylflavonoids from Epimedii Herba and their inhibitory effects on advanced glycation end-products.[Pubmed: 26758618] | Because inhibitors of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), for example pyridoxamine, significantly inhibit the development of retinopathy and neuropathy in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes, treatment with AGE inhibitors is believed to be a potential strategy for the prevention of lifestyle-related diseases such as diabetic complications.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
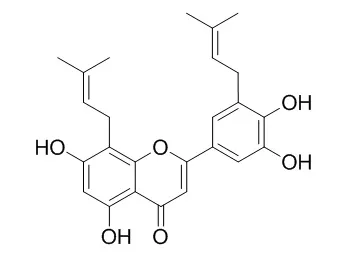
In the present study, the MeOH extract of Epimedii Herba (EH; aerial parts of Epimedium spp.) was found to inhibit the formation of N (ε) -(carboxymethyl)lysine (CML) and N (ω) -(carboxymethyl)arginine (CMA) during incubation of collagen-derived gelatin with ribose. Furthermore, compounds with inhibitory effects against CML and CMA formation were isolated from EH. Two new prenylflavonoids (compounds 1 and 2) and two known compounds (3 and 4) were found to significantly inhibit the formation of both CML and CMA; compound 4 (Epimedokoreanin B) had the strongest inhibitory effect of the isolated compounds.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggest that Epimedokoreanin B could prevent clinical complications of diabetes by inhibiting AGEs. | | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2007 Apr;32(8):715-8. | | Comparison of antioxidative and antitumor activities of six flavonoids from Epimedium koreanum.[Pubmed: 17608228] | To study the antioxidative and antitumor activities of flavonoids isolated from Epimedium koreanum.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were separated by column chromatography with silica gel and Sephadex LH-20, and identified by spectral a- nalysis (ESI-MS, 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR) respectively. DPPH radical scavenging assay and MTT assay were used to observe the antioxidative and antitumor abilities.
Six compounds were isolated from the the ethyl acetate extract of the aerial part. Their structures were identified as icariin (I), luteolin (II), baohuoside II (III), hyperoside (IV), Epimedokoreanin B (V) and baohuoside I (VI). The results indicated that at concentrations of 3. 125-200 micromol x L(-1), compound I, III and VI had no ability to scavenge the DPPH radical, but the scavenging ability of compounds II, IV and V were stronger than that of Vit C in dose-dependant manner. Compounds I, II, V and VI could inhibit the proliferation of MCF-7 and HepG2 in dose-dependant manner, but compounds III and IV had no effect on the proliferation.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antitumor activity of E. koreanum may be partially related to the antioxidantive activity of flavonoids. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)