| In vitro: |
| Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 5;110(6):2258-63. | | Eriocalyxin B ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing Th1 and Th17 cells.[Pubmed: 23345445] | Eriocalyxin B (EriB), a diterpenoid isolated from Isodon eriocalyx, was previously reported to have antitumor effects via multiple pathways, and these pathways are related to immune responses.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we demonstrated that Eriocalyxin B was efficacious in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model for multiple sclerosis. Treatment with Eriocalyxin B led to amelioration of EAE, which correlated with reduced spinal cord inflammation and demyelination. Eriocalyxin B treatment abolished encephalitogenic T-cell responses to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in an adoptive transfer EAE model. The underlying mechanism of Eriocalyxin B-induced effects involved inhibition of T helper (Th) 1 and Th17 cell differentiation through Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator Of Transcription and Nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways as well as elevation of reactive oxygen species.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings indicate that Eriocalyxin B exerts potent antiinflammatory effects through selective modulation of pathogenic Th1 and Th17 cells by targeting critical signaling pathways. The study provides insights into the role of Eriocalyxin B as a unique therapeutic agent for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. | | Exp Hematol. 2010 Mar;38(3):191-201. | | Eriocalyxin B induces apoptosis in lymphoma cells through multiple cellular signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 20045442] | Eriocalyxin B (EriB) is a natural diterpenoid purified from Isodon eriocalyx var. laxiflora and possesses strong antileukemic activity. In this study, we further investigated its effect and mechanism of action in human lymphoma.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In vitro, a series of B- and T-lymphoma cells were treated with Eriocalyxin B. Eriocalyxin B significantly inhibited lymphoma cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in association with caspase activation. Meanwhile, multiple signal transduction pathways were involved in lymphoma cell apoptosis in response to Eriocalyxin B, including inhibition of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB and AKT pathways, and the activation of extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway. ERK activation corresponded to reactive oxygen species production and could be blocked by antioxidant dithiothreitol. In murine xenograft lymphoma models, Eriocalyxin B remarkably inhibited tumor growth and induced in situ tumor cell apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings broaden the value of Eriocalyxin B as a promising candidate targeting apoptosis cascade in treatment of hematological malignancies. | | Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Dec;70(6):1946-55. | | Eriocalyxin B inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activation by interfering with the binding of both p65 and p50 to the response element in a noncompetitive manner.[Pubmed: 16940413 ] | Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) has been recognized to play a critical role in cell survival and inflammatory processes. It has become a target for intense drug development for the treatment of cancer, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we describe a potent NF-kappaB inhibitor, Eriocalyxin B (Eri-B), an ent-kauranoid isolated from Isodon eriocalyx, an anti-inflammatory remedy. The presence of two alpha,beta-unsaturated ketones give this compound the uniqueness among the ent-kauranoids tested. Eri-B inhibited the NF-kappaB transcriptional activity but not that of cAMP response element-binding protein. It suppressed the transcription of NF-kappaB downstream gene products including cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric-oxide synthase induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha or lipopolysaccharide in macrophages and hepatocarcinoma cells. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay indicated that Eri-B selectively blocked the binding between NF-kappaB and the response elements in vivo without affecting the nuclear translocation of the transcription factor. Down-regulation of the endogenous p65 protein sensitized the cells toward the action of the compound. Furthermore, in vitro binding assays suggested that Eri-B reversibly interfered with the binding of p65 and p50 subunits to the DNA in a noncompetitive manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, this study reveals the novel action of a potent NF-kappaB inhibitor that could be potentially used for the treatment of a variety of NF-kappaB-associated diseases. Modification of the structure of this class of compounds becomes the key to the control of the behavior of the compound against different cellular signaling pathways. | | Nat Prod Bioprospect . 2020 Jun;10(3):131-140. | | Eriocalyxin B Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes by Cell Cycle Arrest[Pubmed: 32314168] | | Abstract
Eriocalyxin B, an ent-Kaurene diterpenoid extracted from a traditional Chinese herb Isodon eriocalyx, has been shown to possess multifunctional activities such as anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory. However, the function and mechanism of the compound in adipocyte differentiation is still unknown. Here we reported that Eriocalyxin B blunted adipogenesis remarkably by inhibiting the accumulation of lipid droplets, triglycerides and the expressions of adipogenesis-related factors, including C/EBPβ, C/EBPα, PPARγ, and FABP4. Moreover, we showed that the inhibition might be the consequence of cell cycle being arrested at the G2/M phase during the mitotic clonal expansion of adipocyte differentiation, most likely by suppressing mRNAs and proteins of CDK1, CDK2, Cyclin A and Cyclin B1. Overall, we conclude that Eriocalyxin B is capable of inhibiting adipocyte differentiation at the early stage through downregulating the proteins involved in cell cycle progression.
Keywords: Adipocyte differentiation; Cell cycle; Eriocalyxin B. |
|


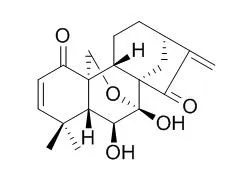



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)