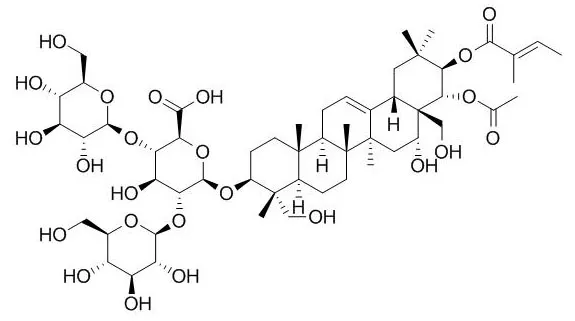
| In vitro: |
| Oncotarget, 2016, 7(17):23684-99. | | Escin Ia suppresses the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via down-regulating LOXL2 expression[Pubmed: 27008697 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The saponin fraction of Aesculus chinensis Bunge fruits (SFAC) could inhibit the invasion and migration of MDA-MB-231 cells. Among which, Escin IA showed more potent inhibition of the invasion than other five main saponin constituents. It selectively reduced the expression of LOXL2 mRNA and promoted the expression of E-cadherin mRNA, and prevented the EMT process of MDA-MB-231 cells and TNF-α/TGF-β-stimulated MCF-7 cells. Moreover, it reduced the LOXL2 level in MDA-MB-231 cells but not in MCF-7 cells. When MCF-7 cells were stimulated with TNF-α/TGF-β, transfected with LOXL2 or treated with hypoxia, Escin IA down-regulated the level of LOXL2 in MCF-7 cells. Meanwhile, Escin IA suppressed the EMT process in LOXL2-transfected or hypoxia-treated MCF-7 cells. Of interest, Escin IA did not alter the level of HIF-1α in hypoxia-induced MCF-7 cells.In TNBC xenograft mice, the metastasis and EMT of MDA-MB-231 cells were suppressed by Escin IA.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Escin IA was the main active ingredient of SFAC for the anti-TNBC metastasis activity, and its action mechanisms involved inhibition of EMT process by down-regulating LOXL2 expression. | | Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2004,36(1):31-5. | | Studies on the biotransformation of escin Ia by human intestinal bacteria and the anti-tumor activities of desacylescin I[Pubmed: 14970884] | To study Biotransformation of Escin IA by the crude enzymes of human intestinal bacteria and Lactobacillus brevis, determine the structures of biotransformation products and assay the inhibitory effect of desacylescin I on the tumor cell growth.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The Escin IA was incubated with crude enzymes of human intestinal bacteria and Lactobacillus brevis in vitro, respectively. The biotransformation products were isolated and purified by the chromatographic methods and the structures were determined by the spectroscopic techniques.
Escin IA was converted into isoEscin IA, desacylescin I, 21beta-O-tigloylprotoaescigenin and protoaescigenin by crude enzymes of human intestinal bacteria and Lactobacillus brevis. Desacylescin I showed potentially inhibitory effects on tumor cell growth of mouse sarcoma-180, hepatic carcinoma H(22) and lung carcinoma in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that Escin IA was a prodrug and its structure can be converted by human intestinal bacteria and Lactobacillus brevis. Desacylescin I as a biotransformation product showed potentially inhibitory effects on mouse tumor, and a potential candidate for anti tumor agents. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)