| Kinase Assay: |
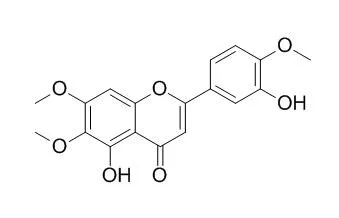
| PLoS One. 2014 Nov 12;9(11):e112536. | | Eupatorin-induced cell death in human leukemia cells is dependent on caspases and activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.[Pubmed: 25390937] | Eupatorin is a naturally occurring flavone that inhibits cell proliferation in human tumor cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here we demonstrate that Eupatorin arrests cells at the G2-M phase of the cell cycle and induces apoptotic cell death involving activation of multiple caspases, mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage in human leukemia cells. This flavonoid induced the phosphorylation of members of the mitogen-activated protein kinases and cell death was attenuated by inhibition of c-jun N-terminal kinases/stress activated protein kinases.
CONCLUSIONS:
Eupatorin-induced cell death is mediated by both the extrinsic and the intrinsic apoptotic pathways and through a mechanism dependent on reactive oxygen species generation. | | Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10(3):R39. | | Antiproliferative and cytostatic effects of the natural product eupatorin on MDA-MB-468 human breast cancer cells due to CYP1-mediated metabolism.[Pubmed: 18454852] | The natural product Eupatorin has been reported to have antiproliferative activity in tumour cell lines, but the exact mechanism is unclear. We aimed to identify a possible mechanism of action for the antiproliferative effect of Eupatorin, which can be attributed to CYP1 family-mediated metabolism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The study focuses on the antiproliferative action of Eupatorin on the human breast carcinoma cell line MDA-MB-468 and on a cell line derived from normal mammary tissue, MCF-10A. The cytotoxicity of the flavone, its effect on the cell cycle of the abovementioned cell lines, and its metabolism by CYP1 family enzymes were examined. Eupatorin showed a dose-dependent inhibitory effect of cell growth on MDA-MB-468 cells with a submicromolar median inhibition concentration (IC50) whereas the IC50 of this compound in MCF-10A cells was considerably higher. Moreover, CYP1 family enzymes were shown to metabolise Eupatorin in vitro to the flavone cirsiliol and two other unidentified metabolites. Metabolism of Eupatorin was also detected in MDA-MB-468 cell cultures, whereas metabolism by MCF-10A cells was negligible. Eupatorin was further shown to arrest the cell cycle of the CYP1-expressing cell line MDA-MB-468 in G2/M phase, whereas no effect was observed in MCF-10A cells, which do not express CYP1 enzymes. The effect of Eupatorin on the MDA-MB-468 cell cycle could be reversed by co-application of the CYP1 inhibitor acacetin.
CONCLUSIONS:
The flavone Eupatorin is selectively activated in breast cancer cells, but not in normal breast cells, due to CYP1 family metabolism. This provides a basis for selectivity which is desired against breast tumour cells. In this sense, Eupatorin is shown by this study to be a very promising chemopreventative candidate that should be examined further in an in vivo study. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2012 Aug;5(4):176-82. | | A simple isocratic HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of sinensetin, eupatorin, and 3'-hydroxy-5,6,7,4'-tetramethoxyflavone in Orthosiphon stamineus extracts.[Pubmed: 22898066 ] | A rapid, specific reversed-phase HPLC method with isocratic elution of acetonitrile: isopropyl alcohol: 20mM phosphate buffer (NaH(2)PO(4)) (30:15:55, v/v) (pH 3.5) at a flow-rate of 1ml/minute, a column temperature of 25°C, and ultraviolet (UV) detection at 340 nm was developed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The method was validated and applied for quantification of different types of O stamineus extracts and fractions. The method allowed simultaneous determination of 3'-hydroxy-5,6,7,4'-tetramethoxyflavone, sinensetin, and Eupatorin in the concentration range of 0.03052-250 μg/ml. The limits of detection and quantification, respectively, were 0.0076 and 0.061 μg/ml for 3'-hydroxy-5,6,7,4'-tetramethoxyflavone, 0.0153 and 0.122 μg/ml for sinensetin and 0.0305 and 0.122 μg/ml for Eupatorin. The percent relative standard deviation (% RSD) values for intraday were 0.048-0.368, 0.025-0.135, and 0.05-0.476 for 3'-hydroxy-5,6,7,4'-tetramethoxyflavone, sinensetin, and Eupatorin, respectively, and those for intraday precision were 0.333-1.688, 0.722-1.055, and 0.548-1.819, respectively. The accuracy for intraday were 91.25%-103.38%, 94.32%-109.56%, and 92.85%-109.70% for 3'-hydroxy-5,6,7,4'-tetramethoxyflavone, sinensetin, and Eupatorin, respectively, and those for interday accuracy were 97.49%-103.92%, 103.58%-104.57%, and 103.9%-105.33%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The method was found to be simple, accurate and precise and is recommended for routine quality control analysis of O stamineus extract containing the three flavonoids as the principle components in the extract. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)