| In vitro: |
| The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 2007, 59(3):463-8. | | Effect of Baccharis dracunculifolia D.C. (Asteraceae) extracts and its isolated compounds on macrophage activation.[Pubmed: 17331351] | Baccharis dracunculifolia D.C. (Asteraceae), a shrub which grows wild in Brazil, is the main botanical source of Brazilian green propolis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
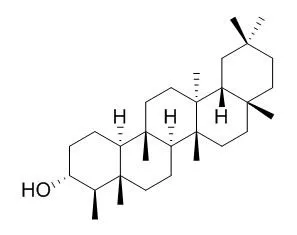
Since Brazilian propolis shows an immunomodulatory activity, the goal of this work was to evaluate the action of B. dracunculifolia extracts and some of its isolated compounds on reactive oxygen intermediate (H(2)O(2)) production by macrophages obtained from male BALB/c mice. The results showed that the leaf (Bd-L) (25, 50, and 100 microg mL(-1)), leaf rinse (Bd-LR) (25 microg mL(-1)), and the root (Bd-R) (25 microg mL(-1)) extracts enhanced H2O2 release by macrophages. A phytochemical study of the root and leaves of B. dracunculifolia was carried out. The chromatographic fractionation of Bd-R, using several techniques, afforded the isolation of baccharis oxide (1), Friedelanol (2), viscidone (11), 11-hydroxy-10,11-dihydro-euparin (12), and 6hydroxy-tremetona (13), while Bd-LR gave the following isolated compounds: baccharis oxide (1), Friedelanol (2), isosakuranetin (3), aromadendrin-4'-methyl ether (4), dihydrocumaric acid (5), baccharin (6), hautriwaic acid lactone (7), hautriwaic acid acetate (8), drupanin (9), and cumaric acid (10). Among the isolated compounds, baccharis oxide (1) and Friedelanol (2) increased H2O2 production at a concentration of 100 microM.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first time that the presence of compounds 7, 8, 12, and 13 in B. dracunculifolia has been reported. Based on these results it is suggested that the crude extracts and some isolated compounds from B. dracunculifolia display an immunomodulatory action. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)