| In vitro: |
| Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2013, 36(7):874-879. | | Dammarane-type saponins from heat-processed Gynostemma pentaphyllum show fortified activity against A549 cells.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
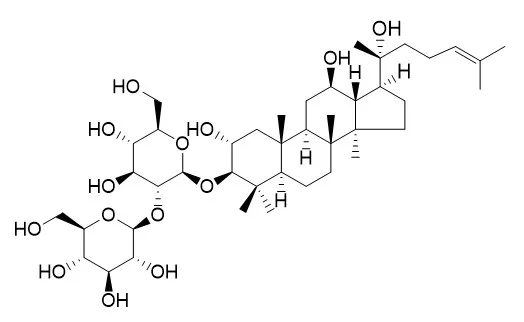
An ethanol extract from heat-processed Gynostemma pentaphyllum showed more potent cytotoxic activity against human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells than that of raw G. pentaphyllum. Four constituents were isolated from heat-processed G. pentaphyllum using resin HP-20, silica gel and reversed ODS column chromatography. They were identified by mass and NMR spectra as damulin A and damulin B, gypenoside L and Gypenoside LI, respectively. To evaluate the efficacy of these four constituents, the MTT cytotoxicity assay was performed using A549 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on the structure of these four constituents, the results indicate that the hydroxyl group in C-2 and double bond in C20(21) and C20(22) positions are of importance in inhibition of A549 cell proliferation. | | Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 12 Mar 2018, 219:161-172. | | The inhibitory effect of gypenoside stereoisomers, gypenoside L and gypenoside LI, isolated from Gynostemma pentaphyllum on the growth of human lung cancer A549 cells.[Pubmed: 29545210 ] | Gypenosides are major constituents in Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino. Previous studies have shown that gypenosides isolated from G. pentaphyllum possess inhibitory effect on the growth of cancer cells, especially A549 cells, with structure-activity relationship (SAR). However, the underlying mechanism of gypenoside-induced A549 cell death remains to be clarified. To further investigate SAR and the underlying mechanism of gypenosides in A549 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Gypenosides were isolated from G. pentaphyllum using chromatography methods and identified using MS and NMR data. The cytotoxicity was determined with CCK-8 assay. The effects of gypenosides on apoptosis, cell cycle and migration were investigated through cell morphology observation, flow cytometry analysis and key proteins detection. Three gypenosides, 2α,3β,12β,20(S)-tetrahydroxydammar-24-ene-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside-20-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, gypenoside L and Gypenoside LI were isolated from G. pentaphyllum. Gypenoside stereoisomers, gypenoside L (S configuration at C20) and Gypenoside LI (R configuration at C20) showed stronger activity against A549 cells. Furthermore, both induced A549 cell apoptosis through intrinsic and extrinsic pathways evidenced by reducing mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), releasing more cytochrome c and down-regulating procaspase 8. However, gypenoside L blocked A549 cells in G0/G1, while Gypenoside LI induced G2/M arrest, which was further verified by different expression of CDK1, CDK2 and CDK4. In addition, both inhibited A549 cell migration, which was evidenced by down-regulation of MMP-2/9 as well as scratch wound assay and transwell assay.
CONCLUSIONS:
C20 of gypenoside played an important role in A549 cell cytotoxicity and gypenoside stereoisomers could be used as potential multi-target chemopreventive agents for cancer. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)