| Animal Research: |
| Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013 Mar;6(3):200-4. | | Homopterocarpin contributes to the restoration of gastric homeostasis by Pterocarpus erinaceus following indomethacin intoxication in rats.[Pubmed: 23375033 ] | To investigate the restorative effect of Pterocarpus erinaceus (P. erinaceus) and Homopterocarpin, an isoflavonoid isolated from it, on indomethacin-induced disruption in gastric homeostasis in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Adult rats were divided into five groups and fasted for 48 h before treatment. Group 1 received olive oil (vehicle), group 2 received 25 mg/kg indomethacin while groups 3-5 received cimetidine (100 mg/kg), Homopterocarpin (25 mg/kg) and P. erinaceus ethanolic stem bark extract (100 mg/kg) respectively. Pretreatment with either Pterocarpus bark extract or Homopterocarpin reversed the effects of indomethacin on the evaluated parameters.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that both Homopterocarpin and Pterocarpus extract offered gastroprotection against indomethacin-induced ulcer by antioxidative mechanism and the modulation of gastric homeostasis. The results also suggest that Homopterocarpin might be responsible for, or contribute to the antiulcerogenic property of P. erinaceus. | | Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2006 Aug;70(8):1864-8. | | Insect antifeedants, pterocarpans and pterocarpol, in heartwood of Pterocarpus macrocarpus Kruz.[Pubmed: 16926498 ] | The insect antifeedant activities of pterocarpans and a sesquiterpene alcohol from the dichloromethane extract of Pterocarpus macrocarpus Kruz. (Leguminosae) were evaluated against the common cutworm, Spodoptera litura F. (Noctuidae), and the subterranean termite, Reticulitermes speratus (Kolbe)(Rhinotermitidae).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
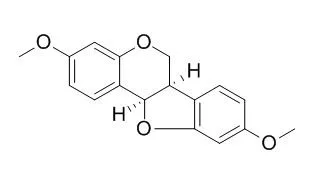
Three pterocarpans, (-)-Homopterocarpin (1), (-)-pterocarpin (2), and (-)-hydroxyHomopterocarpin (3) and the sesquiterpene alcohol, (+)-pterocarpol (5), were isolated from the dichloromethane extract of the heartwood of P. macrocarpus under guidance by a biological assay. Among these natural products, the most active insect antifeedant against both S. litura and R. speratus was 1. On the other hand, sesquiterpene alcohol 5 showed less insect antifeedant activity than the other pterocarpans against both insect species. While its methylated derivative, (-)-methoxyHomopterocarpin (4), showed high biological activity, 3 showed less insect antifeedant activity in this study.
CONCLUSIONS:
Interestingly, racemic 1 did not show insect antifeedant activity against S. litura. However, all of the test pterocarpans and isoflavones showed antifeedant activity against the test termites.
Additionally, since these compounds were major constituents of P. macrocarpus, these antifeedant phenolics may act as chemical defense factors in this tree. In Thailand, lumber made from this tree is used to make furniture and in building construction due to its resistance to termite attack. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)