| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of the science of food and agriculture, 2019, 99:págs. 1475-1483. | | The relationship between alkylamide compound content and pungency intensity of Zanthoxylum bungeanum based on sensory evaluation and ultra‐performance liquid chromatography‐mass spectrometry/ mass spectrometry (UPLC‐MS/MS) analysis.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The pungency intensity of 19 Zanthoxylum bungeanum samples was first determined with Scoville pungency units (SPUs). The SPUs were found to range from 3.80E + 04 to 5.40E + 05. The chemical compositions and contents were measured next, using the ultra‐performance liquid chromatography‐mass spectrometry/ mass spectrometry (UPLC‐MS/MS) method. The total alkylamide content ranged from 9.83 ± 0.15 to 89.98 ± 1.35 g kg−1. Hydroxy‐ϵ‐sanshool, hydroxy‐α‐sanshool, Hydroxy-beta-sanshool, Hydroxy-γ-sanshool(Hydroxy-gamma-sanshool), bungeanool, and isobungeanool were found to be the key pungent compounds, ranging in proportion from 92.65% to 97.69%. The relationship between alkymide compound content and pungency intensity was also analyzed by ridge regression, and it was found that the β values of independent variables were stable when k was more than 0.6. The regression coefficients of hydroxy‐ϵ‐sanshool, hydroxy‐α‐sanshool, hydroxy‐β‐sanshool, hydroxy‐γ‐sanshool, bungeanool, isobungeanool, and other alkylamides were 0.105, 0.177, 0.386, −0.166, −0.006, 0.005, and −0.018, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Hydroxy‐ sanshool compounds were important in determinant the pungency intensity of Z. bungeanum. Knowledge of the relationship between alkymide compound content and pungency intensity will assist in the creation of new methods to determine pungency intensity and provide a scientific basis for flavor design, development of pungent food products, and consumer choice evaluations. | | Planta Med. 1990 Feb;56(1):89-91. | | Lignans and other constituents from South and central american zanthoxylum species.[Pubmed: 17221375 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
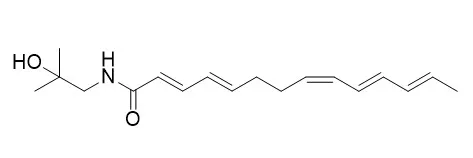
Eight lignans (+/-)-syringaresinol, (-)-pinoresinol, (+)-sesamin, (+)-eudesmin, (+)-epieudesmin, (-)-asarinin, (-)-matairesinol, (-)-kobusin, two terpenes lupeol, beta-sitosterol, one aliphatic unsaturated amide, Hydroxy-gamma-sanshool(Hydroxy-γ-sanshool), and one alkaloid, magnoflorine, were isolated from ZANTHOXYLUM species of Central and South America.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Their structures were elucidated mainly by (1)H-, (13)C-NMR, and mass spectroscopy. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)