| Kinase Assay: |
| Inflammation. 2011 Oct;34(5):344-51. | | Kakkalide and its metabolite irisolidone ameliorate carrageenan-induced inflammation in mice by inhibiting NF-κB pathway.[Pubmed: 20686830] | The anti-inflammatory activities of Kakkalide, a major constituent of the flower of Pueraria thunbergiana, and irisolidone, a metabolite of Kakkalide produced by intestinal microflora, against carrageenan-induced inflammation in air pouches on the backs of mice and in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated peritoneal macrophages were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Kakkalide and irisolidone down-regulated the gene expression of cytokines [tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β)] and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-1β, and inflammatory mediators, NO and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)), in LPS-stimulated peritoneal macrophages. These agents also inhibited the phosphorylation of IκB-α and the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB). Orally administered Kakkalide and irisolidone significantly reduced carrageenan-induced inflammatory markers, leukocyte number, and protein amount in the exudates of the air pouch. These constituents also inhibited PGE(2) production and COX-2 inducible nitric oxide synthase, IL-1β, and TNF-α expression. These agents also inhibited NF-κB activation. The anti-inflammatory effects of irisolidone were more potent than those of Kakkalide.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on these findings, Kakkalide and irisolidone may inhibit inflammatory reactions via NF-κB pathway, and irisolidone, a metabolite of Kakkalide, may more potently inhibit these inflammatory reactions. |
|
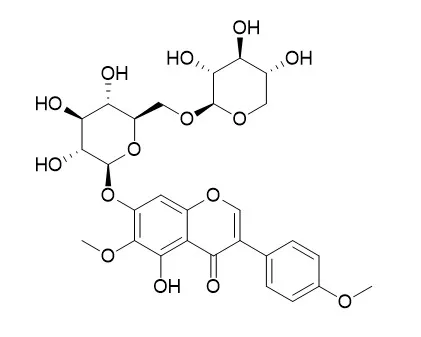
| Structure Identification: |
| J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017 Mar 24;1048:111-120. | | Extraction and isolation of potential anti-stroke compounds from flowers of Pueraria lobata guided by in vitro PC12 cell model.[Pubmed: 28236683] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A simple and efficient method based on ultrafiltration liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UFLC-MS) was applied to rapidly screen and identify ligands for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) from the flowers of Pueraria lobata, and the compounds were assessed for anti-stroke activity using a PC12 cell model. Seven major isoflavones, Kakkalide, 3'-hydroxy puerarin, puerarin, puerarin xyloside, tectoridin, tectorigenin, and ononin, were identified as potent LDH inhibitors. A continuous online method, which consisted of microwave-assisted extraction and countercurrent chromatography (MAE-CCC), was newly developed for scaled-up production of these compounds with high purity and efficiency.
CONCLUSIONS:
This novel approach, using UFLC-MS coupled with MAE-CCC and a PC12 cell model, provided a powerful tool for screening, extraction, and separation of LDH inhibitors from complex samples, and a useful platform for the large-scale production of functional food and nutraceutical ingredients. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)