| Kinase Assay: |
| Biomed Chromatogr. 2016 Nov;30(11):1843-1853. | | Screening and identification of Caulis Sinomenii bioactive ingredients with dual-target NF-κB inhibition and β2- AR agonizing activities.[Pubmed: 27187693] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
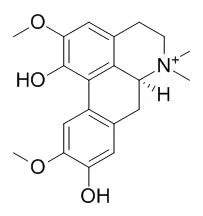
Seven potential NF-κB inhibitors were identified, including laudanosoline-1-O-xylopyranose, 6-O-methyl-laudanosoline-1-O-glucopyranoside, menisperine, sinomenine, Laurifoline, magnoflorine and norsinoacutin. Furthermore, IL-6 and IL-8 assays confirmed the anti-inflammatory effects of these potential NF-κB inhibitors, in which laudanosoline-1-O-d-xylopyranose and menisperine were revealed as novel NF-κB inhibitors. Among the seven identified alkaloids, three potential β2 -adrenergic receptor agonists, including sinomenine, magnoflorine and Laurifoline, were characterized using a luciferase reporter system to measure for the activity of β2 -adrenergic receptor agonists. Finally, sinomenine, magnoflorine and Laurifoline were identified not only as potential NF-κB inhibitors but also as potential β2 -adrenegic receptor agonists, which is the first time this has been reported.
CONCLUSIONS:
Molecular dynamic simulation and docking results suggest that the three dual-bioactive constituents could not only inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK strain-induced inflammatory responses via a negative regulation of the Braf protein that participates in MAPK signaling pathway but also activate the β2 -adrenegic receptor. These results suggest that CS extract has dual signaling activities with potential clinical application as a novel drug for asthma. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| J Chromatogr A. 2012 Jul 27;1248:93-103. | | Tissue-specific metabolite profiling of alkaloids in Sinomenii Caulis using laser microdissection and liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time of flight-mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 22721764] | Secondary metabolites accumulated in different tissues and cells of herbs are usually bioactive components of herbal medicines. Thus, tissue- and cell-specific phytochemical profiling should be useful for indicating relationship between herbal tissues and chemicals, and evaluating the quality of a medicinal herb.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, a method that combining laser microdissection and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LMD with UPLC-Q/TOF-MS) was established to achieve simultaneous localization and determination of bioactive components in herbal medicines. Sinomenii Caulis, sourced from the stems of Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehd. et Wils., was set as an illustrative case, and its phytochemicals were profiled by the present method through analyses of different microdissected tissues and cells, involving epidermis, cortex, stone cells, pericycle, vascular bundles and pith. Results revealed that different tissues and cells contained varied alkaloids, among which six alkaloids, i.e. 6-Me-ether-12-O-β-D-glucopyranoside-laudanosoline (peak 4), sinomenine (peak 6), N-norsinoacutine (peak 7), magnoflorine (peak 11), Laurifoline (peak 16) and menisperine (peak 17) were detected in all microdissected parts, and sinomenine and magnoflorine were the two most abundant components. By further quantitative determination, alkaloids were generally demonstrated to distribute in the outer part of the cortex, phloem and xylem.
CONCLUSIONS:
According to the relationship between alkaloids and tissues revealed in our study, Sinomenii Caulis of larger diameter has proportionately more bioactive components, and is therefore of higher quality for medicinal use. The method of LMD with UPLC-Q/TOF-MS developed in this study was initially applied to the research of medicinal herbs, and proved to be high sensitive, low cost, convenient and practical. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)