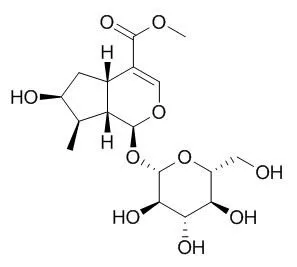
| Description: |
Loganin is a non-competitive inhibitor of BACE1 with IC50 of 47.97 μM an also inhibits AChE and BChE with IC50 values of 3.95 μM and 33.02 μM, respectively. Loganin has neuroprotective, anti-amnesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-shock effects, it also exhibits protective effects against hepatic injury and other diabetic complications associated with abnormal metabolic states and inflammation caused by oxidative stress and advanced glycation endproduct formation. Loganin can attenuate neuroinflammatory responses through the inactivation of NF-κB by NF-κB dependent inflammatory pathways and phosphorylation of MAPK in Aβ25-35-induced PC12 cells, and can protect against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by inhibiting phosphorylation of JNK, p38, and ERK 1/2 MAPKs in SH-SY5Y cells. |
| Targets: |
NF-kB | Beta Amyloid | p38MAPK | TNF-α | NOS | COX | ROS | ERK | JNK | IkB | PARP | Bcl-2/Bax | IKK |
| In vitro: |
| Neurochem Int. 2011 Mar;58(4):533-41 | | Loganin protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by inhibiting phosphorylation of JNK, p38, and ERK 1/2 MAPKs in SH-SY5Y cells.[Pubmed: 21241762] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the mechanisms underlying the protective effects of Loganin against hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2))-induced neuronal toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. The neuroprotective effect of Loganin was investigated by treating SH-SY5Y cells with H(2)O(2) and then measuring the reduction in H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis using 3-(4,5-dimethyl thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assays. Following H(2)O(2) exposure, Hoechst 33258 staining indicated nuclear condensation in a large proportion of SH-SY5Y cells, along with an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and an intracellular decrease in mitochondria membrane potential (MMP). Loganin was effective in attenuating all the above-stated phenotypes induced by H(2)O(2). Pretreatment with Loganin significantly increased cell viability, reduced H(2)O(2)-induced LDH release and ROS production, and effectively increased intracellular MMP. Pretreatment with Loganin also significantly decreased the nuclear condensation induced by H(2)O(2). Western blot data revealed that Loganin inhibited the H(2)O(2)-induced up-regulation of cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and cleaved caspase-3, increased the H(2)O(2)-induced decrease in the Bcl-2/Bax ratio, and attenuated the H(2)O(2)-induced release of cytochrome c from mitochondria to the cytosol. Furthermore, pretreatment with Loganin significantly attenuated the H(2)O(2)-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK 1/2).
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the protective effects of Loganin against H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis may be due to a decrease in the Bcl-2/Bax ratio expression due to the inhibition of the phosphorylation of JNK, p38, and ERK 1/2 MAPKs. Loganin's neuroprotective properties indicate that this compound may be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Life Sci. 2015 Feb 15;123:78-85. | | Loganin attenuates diabetic nephropathy in C57BL/6J mice with diabetes induced by streptozotocin and fed with diets containing high level of advanced glycation end products.[Pubmed: 25623853] | Diabetic nephropathy is the most common cause of end-stage renal disease in patients with diabetes. Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) play a prominent role in the development of diabetic nephropathy. We herein evaluated the effects of Loganin on diabetic nephropathy in vivo.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We established a diabetic nephropathy model in C57BL/6J mice with diabetes induced by streptozotocin and fed with diets containing high level of AGEs. Diabetic symptoms, renal functions, and pathohistology of pancreas and kidney were evaluated. AGE-RAGE pathway and oxidative stress parameters were determined. The model mice exhibited characteristic symptoms of diabetes including weight loss, polydipsia, polyphagia, polyuria, elevated blood glucose levels and low serum insulin levels during the experiments. However, Loganin at doses of 0.02 and 0.1g/kg effectively improved these diabetic symptoms. Loganin reduced kidney/body weight ratio, 24h urine protein levels, and serum levels of urea nitrogen and creatinine in diabetic mice to different degrees compared to positive controls. Moreover, Loganin improved the histology of pancreas and kidney, and alleviated the structural alterations in endothelial cells, mesangial cells and podocytes in renal cortex. Finally, we found that Loganin reduced AGE levels in serum and kidney and downregulated mRNA and protein expression of receptors for AGEs in kidney in diabetic mice. Loganin also reduced the levels of malondialdehyde and increased the levels of superoxide dismutase in serum and kidney.
CONCLUSIONS:
Loganin improved diabetic nephropathy in vivo associated with inhibition of AGE pathways, and could be a promising remedy for diabetic nephropathy. | | Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Oct 1;619(1-3):44-9. | | Loganin improves learning and memory impairments induced by scopolamine in mice.[Pubmed: 19666019 ] | Loganin is an iridoid glycoside found in the Flos lonicerae, Fruit cornus, and Strychonos nux vomica.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effect of Loganin on learning and memory impairments induced by scopolamine (0.5mg/kg, i.p.), a muscarinic antagonist, using the Y-maze, passive avoidance, and the Morris water maze tests in mice. In the Y-maze test, Loganin (40 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly improved the scopolamine-induced memory impairment. In addition, Loganin (20 and 40 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly reversed scopolamine-induced impairments measured by the passive avoidance and the Morris water maze tests. A day after the last trial session of the Morris water maze test (probe trial session), Loganin (20 and 40 mg/kg) dose-dependently increased the latency time in the target quadrant. Furthermore, Loganin significantly inhibited acetylcholinesterase activity in the hippocampus and frontal cortex.
CONCLUSIONS:
Loganin may have anti-amnesic activity that may hold significant therapeutic value in alleviating certain memory impairments observed in Alzheimer's disease. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)