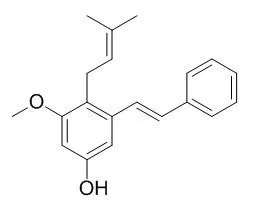
| Structure Identification: |
| Chin J Nat Med. 2015 Apr;13(4):311-5. | | Synthesis and cytotoxicity of longistylin C derivatives.[Pubmed: 25908631] | The present study was designed to identify potent anti-tumor compounds from a series of new Longistylin C derivatives.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ten Longistylin C derivatives were synthesized and their structures were confirmed by (1)H NMR, MS, and elemental analyses. Their cytotoxicity in vitro against three human cancer cell lines (A549, HepG2, and MCF-7) were evaluated by the MTT assay. Among these compounds, DT-6 and DT-9 displayed much better cytotoxicity against A549, HepG2, and MCF-7 cells, DT-1 exhibited selective cytotoxicity against HepG2, and the structure-activity relationships were investigated.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Compounds DT-6 and DT-9 may serve as potential lead compounds for the discovery of new anti-cancer drugs. | | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Oct;36(19):2680-3. | | Determination of longistylin A and longistylin C in Cajanus cajan.[Pubmed: 22242429] | To establish quality control criteria for medicinal herb Cajanus cajan based on the determination of longistylin A and Longistylin C, two bioactive and specific stilbenes of the plant.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Longistylin A and Longistylin C were obtained from the leaves of C. cajan by silica gel column chromatography and identified as marker compounds of this plant by spectroscopic analysis. A RP-HPLC method was established to determine the two compounds.
Longistylin A and Longistylin C were well separated on a Thermo BDS Hypersil C18 column (4.6 mm x 250 mm, 5 microm) with a mobile phase methanol-water (8:2), and showed good linearity in the range of 0.00288 - 0.0576 microg and 0.0112 - 0.224 microg, respectively. The average recoveries were 98.9% and 97.2% with RSD of 2.4% and 2.2% for these two compounds, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The established analysis method is simple and accurate, whicn can be used for quality control of C. cajan. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)