| In vitro: |
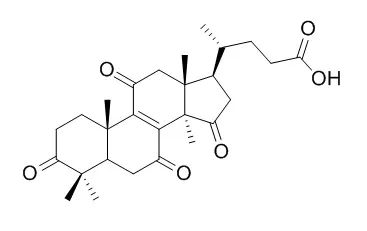
| J Nat Prod. 2003 Dec;66(12):1582-5. | | Lucidenic acids P and Q, methyl lucidenate P, and other triterpenoids from the fungus Ganoderma lucidum and their inhibitory effects on Epstein-Barr virus activation.[Pubmed: 14695801 ] | A new triterpene acid, lucidenic acid P (1a), and two new triterpene acid methyl esters, methyl lucidenates P (1b) and Q (2b), were isolated and characterized from the fruiting body of the fungus Ganoderma lucidum.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods. In addition, eight known triterpene acids, lucidenic acid A (3a), lucidenic acid C (4a), lucidenic acid D(2) (5a), lucidenic acid E(2) (6a), and Lucidenic acid F (7a) and ganoderic acid E (9a), lganoderic acid F (10a), and ganoderic acid T-Q (11a), and six known triterpene acid methyl esters, methyl lucidenates A (3b), D(2) (5b), E(2) (6b), F (7b), and L (8b) and methyl ganoderate F (10b), were isolated and identified from the fungus.
All of the triterpenoids, with the exception of 7a, were evaluated with respect to their inhibitory effects on the induction of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) in Raji cells, which is known to be a primary screening test for antitumor promoters.
CONCLUSIONS:
All of the compounds tested showed potent inhibitory effects on EBV-EA induction (96-100% inhibition at 1 x 10(3) mol ratio/TPA). | | Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Apr 29;408(1):18-24. | | Lucidenic acids-rich extract from antlered form of Ganoderma lucidum enhances TNFα induction in THP-1 monocytic cells possibly via its modulation of MAP kinases p38 and JNK.[Pubmed: 21453678 ] | The Ganoderma lucidum (G. lucidum) is one of the oriental fungi that has been reported to have immunomodulatory properties. Although effect of β-glucans from G. lucidum has been well documented, little is known about how other major bioactive components, the triterpenes, contribute to the immunomodulatory function of G. lucidum.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we showed that triterpenes-rich extract of antlered form of G. lucidum (G. lucidum AF) induces TNFα production in monocytic THP-1 cells. Furthermore, the extract also synergized with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce TNFα production in THP-1 cells, suggesting an immunostimulatory role of triterpenes-rich extract of G. lucidum AF. Notably, the extract enhanced LPS-induced phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), while it suppressed LPS-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) MAPK. p38 Inhibitor suppressed TNFα production, while JNK inhibitor enhanced TNFα production, implying that synergistic effect of the extract may work by modulating p38 and JNK MAPKs. Moreover, we found that the triterpenes-rich extract of G. lucidum AF contains high amounts of lucidenic acids. Lucidenic acid-A, -F and -D(2), which seem to dominantly exist in the extract, were purified from the triterpenes-rich extract. We also identified Lucidenic acid A and Lucidenic acid F as modulators of JNK and p38, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, our data demonstrate that lucidenic acids-rich extract from G. lucidum AF enhances LPS-induced immune responses in monocytic THP-1 cells possibly via the modulation of p38 and JNK MAPKs activation. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)