| Cell Research: |
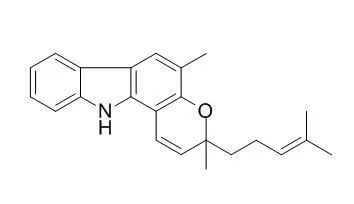
| Phytother Res. 2010 Apr;24(4):629-31. | | Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory potential of a carbazole alkaloid, mahanimbine, from Murraya koenigii.[Pubmed: 19943242] | Stem barks of Mangifera indica contain a rich content of mangiferin (xanthone glucoside), whereas Murraya koenigii leaves contain rich sources of Mahanimbine (carbazole alkaloid) and used traditionally for the treatment of diabetes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the search for acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors from Indian medicinal plants, via bioassay-guided isolation, a carbazole alkaloid, Mahanimbine [3, 5-dimethyl-3-(4- methylpent-3-enyl)-11H-pyrano [5, 6-a] carbazole], was isolated from the petroleum ether extract of the leaves of Murraya koenigii. Inhibition of AChE was evaluated based on Ellman's method using 96-well microplate readers. Mahanimbine inhibited AChE activity in a dose-dependent manner with an IC(50) value of 0.03 +/- 0.09 mg/mL, while galantamine was used as a standard.
CONCLUSIONS:
The AChE inhibitory activity of this carbazole alkaloid has not been reported so far, and this study is the first to reveal this activity in carbazole alkaloid Mahanimbine, isolated from Murraya koenigii. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Biofactors. 2017 Mar;43(2):220-231. | | Effect of mahanimbine, an alkaloid from curry leaves, on high-fat diet-induced adiposity, insulin resistance, and inflammatory alterations.[Pubmed: 27663177 ] | Spices and condiments, small but an integral part of the daily diet, are known to affect physiological functions. This study evaluated the effects of Mahanimbine, a major carbazole alkaloid from Murraya koenigii (curry leaves), against progression of high-fat diet (HFD)-induced metabolic complications in mice (male and female).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Mahanimbine at 2 mg/kg (HFD + LD) and 4 mg/kg (HFD + HD) of body weight was administered daily along with HFD feeding for 12 weeks. At the end of the study, male HFD + LD and HFD + HD groups showed 51.70 ± 3.59% and 47.37 ± 3.73% weight gain, respectively, as compared with 71.02 ± 6.04% in HFD fed mice whereas female HFD + LD and HFD + HD groups showed 24.31 ± 1.68% and 25.10 ± 2.61% weight gain as compared with HFD group with 36.69 ± 3.60% of weight gain. Mahanimbine prevented HFD-induced hyperlipidemia and fat accumulation in adipose tissue and liver along with the restricted progression of systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. Moreover, Mahanimbine treatment improved glucose clearance and upregulated the expression of insulin responsive genes in liver and adipose tissue. Male and female mice showed different traits in development of HFD-induced metabolic disturbances; however, Mahanimbine treatment exerted similar effects in both the sexes. In addition, Mahanimbine lowered the absorption of dietary fat resulting in dietary fat excretion.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, daily consumption of Mahanimbine and thereby curry leaves may alleviate development of HFD-induced metabolic alterations. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)