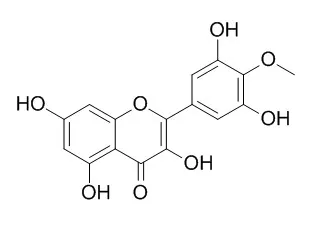
| Structure Identification: |
| Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2011 Jun;79(1):282-93. | | Antioxidant behavior of mearnsetin and myricetin flavonoid compounds--a DFT study.[Pubmed: 21420896 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The molecular characteristics of two naturally occurring flavonoid compounds Mearnsetin and myricetin have been computed using density functional theory (DFT) approach with B3LYP/6-311G(d,p) level of theory. The computation and analysis of bond dissociation enthalpy magnitudes for all the OH sites for both the compounds clearly denotes the contribution of the B-ring for the antioxidant activity. The analysis has also indicated the higher values of BDE on the C5-OH radical species in both the compounds. The computed vibrational frequency analysis indicates the absence of imaginary frequency in the neutral as well as radical species of both the flavonoid compounds. The ionisation potential (IP) analysis was found to be within the range of the IP of synthetic food additives. In addition, various molecular descriptors such as electron affinity, hardness, softness, electronegativity, electrophilic index have also been calculated and the validity of Koopman's theorem is verified.
The plot of frontier molecular orbital and spin density distribution analysis for neutral and the corresponding radical species for both the compounds have been computed and interpreted.
CONCLUSIONS:
The polar nature and their polarizing capacity are well established through the analysis of dipole moment and polarisability magnitudes. | | J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Sep 14;59(17):9386-93. | | Characterization of phenolic components in polar extracts of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. bark by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 21761864 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
High-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS) and tandem mass spectrometry (MS(n)) were used to investigate the phenolic constituents in methanol, water, and methanol/water extracts of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. bark. Twenty-nine phenolic compounds were identified, 16 of them referenced for the first time as constituents of E. globulus bark, namely, quinic, dihydroxyphenylacetic, and caffeic acids, bis(hexahydroxydiphenoyl (HHDP))-glucose, galloyl-bis(HHDP)-glucose, galloyl-HHDP-glucose, isorhamentin-hexoside, quercetin-hexoside, methylellagic acid (EA)-pentose conjugate, myricetin-rhamnoside, isorhamnetin-rhamnoside, Mearnsetin, phloridzin, Mearnsetin-hexoside, luteolin, and a proanthocyanidin B-type dimer. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)