| In vitro: |
| Plant Sci . 2013 Sep;210:61-9. | | Metabolite profiling of the short-term responses of rice leaves (Oryza sativa cv. Ilmi) cultivated under different LED lights and its correlations with antioxidant activities[Pubmed: 23849114] | | Abstract
Metabolite profiling of rice leaves (Oryza sativa cv. Ilmi) was performed to investigate the short-term responses to different light-emitting diode (LED) lights, blue (B), green (G), red (R), white (W), shade (S), by using gas chromatography-ion trap-mass spectrometry (GC-IT-MS) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) with multivariate analysis. Clear grouping patterns of each light-grown sample, except G and W, were shown in partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA). Thirty-two primary metabolites and eleven secondary metabolites were selected and visualized using heatmap. Antioxidant activities of rice leaves followed the order B=W=G>R>S and isoorientin-2''-O-glucoside, isovitexin-2''-O-glucoside, isoorientin-2''-O-(6'''-ρ-coumaroyl)-glucoside, and isoscoparin-2''-O-glucoside showed similar relative differences and had higher Pearson's correlation coefficients than other metabolites in correlation network. According to the orthogonal projection to latent structures-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) between B and R, the levels of amino acids, organic acids, fatty acids, and flavonoid glycosides were relatively high in B, whereas the glucose and fructose levels were high in R.
Keywords: Antioxidant activity; GC–IT-MS; LED lights; Metabolite profiling; Oryza sativa; UPLC–Q-TOF-MS. | | Phytochemistry . 2018 Apr;148:11-20. | | Changes in isovitexin-O-glycosylation during the development of young barley plants[Pubmed: 29421507] | | Abstract
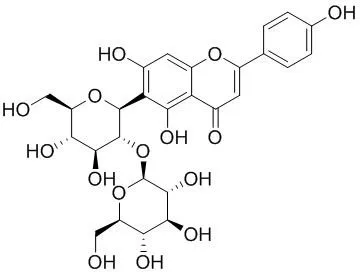
Phenylpropanoids are a class of plant natural products that have many biological functions, including stress defence. In barley, phenylpropanoids have been described as having protective properties against excess UV-B radiation and have been linked to resistance to pathogens. Although the phenylpropanoid composition of barley has recently been addressed in more detail, the biosynthesis and regulation of this pathway have not been fully established. Barley introgression lines, such as the S42IL-population offer a set of genetically diverse plants that enable the correlation of metabolic data to distinct genetic regions on the barley genome and, subsequently, identification of relevant genes. The phenylpropanoid profiles of the first and third leaf of barley seedlings in Scarlett and four members of the S42IL-population were obtained by LC-MS. Comparison of the leaf profiles revealed a change in the glycosylation pattern of the flavone-6-C-glucoside isovitexin in the elite cultivar Scarlett. The change was characterized by the stepwise decrease in isovitexin-7-O-glucoside (saponarin) and an increase in isovitexin-2″-O-β-D-glucoside content. The lines S42IL-101-, -177 and -178 were completely devoid of isovitexin-2″-O-β-D-glucoside. Parallel glucosyltransferase assays were consistent with the observed metabolic patterns. The genetic region responsible for this metabolic effect was located on chromosome 1H between 0.21 and 15.08 cM, encompassing 505 gene candidates in the genome of the sequenced cultivar Morex. Only one of these genes displayed sequence similarity with glucosyltransferases of plant secondary metabolism that possessed the characteristic PSPG motif.
Keywords: 441381); Barley introgression lines; Flavonoids; Hordeum vulgare spp. vulgare; Isovitexin-2″-O-β-D-glucoside; Isovitexin-2″-O-β-D-glucoside (PubChem CID: 25202838); Isovitexin-7-O-glucoside; Isovitexin-7-O-glucoside (PubChem CID:; LC-MS; Metabolite profiling; Morex; Phenylpropanoids; Poaceae; Scarlett. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)